-
 Collaborative software
Collaborative software
-
 e-Couponing
e-Couponing
-
 Molecule
Molecule
-
 STN
STN
-
 IFREMER
IFREMER
-
 Wood pellets
Wood pellets
-
 Processor frequency
Processor frequency
-
 PCR
PCR
-
 AIFF
AIFF
-
 Evaporitic
Evaporitic
-
 Atrophy
Atrophy
-
 Convection
Convection
-
 Magma chamber
Magma chamber
-
 Continental slope
Continental slope
-
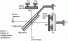 Michelson interferometer
Michelson interferometer
-
 Flagellum
Flagellum
-
 Common broom
Common broom
-
 Gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
-
 EUMETSAT
EUMETSAT
-
 Coenzyme
Coenzyme
-
 Constellation of Capricorn
Constellation of Capricorn
-
 Isomerase
Isomerase
-
 Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande
-
 Fractal
Fractal
-
 Apricot
Apricot
-
 Intestinal absorption inhibitor
Intestinal absorption inhibitor
-
 IPv4
IPv4
-
 Onco-haematologist
Onco-haematologist
-
 Glass
Glass
-
 Wetland
Wetland
Echolocation
Echolocation is a system of location and identification used by some animals: bats, a few cetaceans (killer whales, dolphins), a few birds and shrews.
In bats this system replaces poor or non-existent vision, while in dolphins, for example, it complements the animal's vision.

Echolocation principle. © Malene Thyssen, Wikipedia, cc by sa 2.5
This system is based on the physical properties of sound waves. The animal sends waves by clicking its tongue or otherwise. These waves bounce off all obstacles found in the emitting animal's environment (see the animation above) then return to the source (ears in Chiropters), giving the animal a three-dimensional image of its environment.
 Bats use echolocation to navigate. © Jan Svetlík, Flickr, cc by nc nd 2.0
Bats use echolocation to navigate. © Jan Svetlík, Flickr, cc by nc nd 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



