-
 GPS
GPS
-
 Electroencephalogram
Electroencephalogram
-
 PCR
PCR
-
 Breast cancer
Breast cancer
-
 Granulocytopenia
Granulocytopenia
-
 Kelvin
Kelvin
-
 Angiotensin
Angiotensin
-
 Tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane
-
 Climber
Climber
-
 Amylose
Amylose
-
 Urogenital system
Urogenital system
-
 Rare earth minerals
Rare earth minerals
-
 Camouflage feathers
Camouflage feathers
-
 Nintendo Revolution
Nintendo Revolution
-
 Fluorine
Fluorine
-
 African clawed frog
African clawed frog
-
 Alar
Alar
-
 World Charter for Nature
World Charter for Nature
-
 Glinide
Glinide
-
 Constellation of Leo
Constellation of Leo
-
 Cerebrovascular accident
Cerebrovascular accident
-
 Open cluster
Open cluster
-
 Biguanide
Biguanide
-
 Food bolus
Food bolus
-
 Turbopump
Turbopump
-
 Organic agriculture
Organic agriculture
-
 Expansion valve
Expansion valve
-
 Flocking
Flocking
-
 Neoformation
Neoformation
-
 Cryogenian
Cryogenian
Ulysses
The ULYSSES probe is a joint ESA and NASA mission, devoted to the in situ study of turbulence in the solar wind, especially outside the ecliptic plane. Its instruments were designed and manufactured by European and American scientists. Several European laboratories took part in the development of Ulysses. The ULYSSES probe was launched on board the space shuttle Discovery from Cape Canaveral, USA, on 6 October 1990.

The Ulysses probe
(Credits: ESA)
The objective of the ULYSSES is to:
- Determine the overall three-dimensional properties of the heliospheric magnetic field and the solar wind;
- study the origins of solar wind by measuring its composition at different heliographic latitudes;
- increase our knowledge of shock waves in the solar wind by sampling the conditions from those measured near to the ecliptic;
- increase our knowledge of processes affecting the movement of abnormal and galactic cosmic rays;
- increase our knowledge of the origin of galactic cosmic rays by measuring their isotopic composition;
- study the energy level and movement of the energetic particles of solar and interplanetary origin by observing their properties at low and high latitudes;
- learn more about nearby interstellar space medium by direct measurements of the neutral helium atoms that enter the heliosphere, as well as by deducing their properties from measurements of interstellar ions;
- improve our knowledge about interplanetary and interstellar dust;
- search for sources of gamma bursts and, using simultaneous observations from other satellites, help to identify them in relation to known celestial objects.
The ULYSSES probe is equipped with twelve instruments:
- VHM/FGM: The Vector Helium Magnetometer / Flux Gate Magnetometer; the French CETP (Centre d'Etude des Environnements Terrestre et Planetaires) participated in this project;
- SWOOPS (Solar Wind Plasma experiment): a solar wind plasma experiment, the CETP participated;
- SWICS (Solar Wind Ion Composition Instrument);
- URAP (Unified Radio and Plasma Wave instrument): an experiment to measure radio waves and plasma in the inner heliosphere, carried out jointly by 4 laboratories: the NASA/GSFC Laboratory for Extraterrestrial Physics (LEP), the Paris Observatory LESIA, the University of Minnesota and the CETP at Vélizy;
- EPAC (Energetic Particle Instrument);
- GAS (Interstellar Neutral-Gas Experiment);
- HISCALE (Low-energy Ion and Electron Experiment) in which the LESIA also participated;
- COSPIN (Cosmic Ray and Solar Particle Instrument)
- DUST (Dust Experiment) ;
- SCE (Coronal-Sounding Experiment);
- GWE (Gravitational Wave Experiment).
GRB (Solar X-ray and Cosmic Gamma-Ray Burst Instrument);
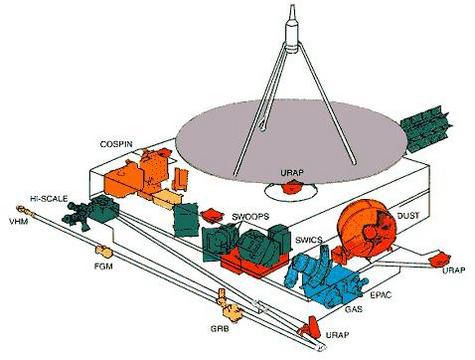 The Ulysses probe instruments.
(Credits: ESA)
The Ulysses probe instruments.
(Credits: ESA)
Latest
Fill out my online form.



