-
 MA
MA
-
 Albinism
Albinism
-
 Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
-
 Amylose
Amylose
-
 Emollient
Emollient
-
 Nonlinear crystal
Nonlinear crystal
-
 Septicaemic plague
Septicaemic plague
-
 Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
-
 Mara des bois
Mara des bois
-
 Fog
Fog
-
 Dopaminergic agonist
Dopaminergic agonist
-
 Phase transition
Phase transition
-
 Pear
Pear
-
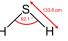 Hydrogen sulphide
Hydrogen sulphide
-
 Semantic web
Semantic web
-
 Mutagen
Mutagen
-
 Hadean
Hadean
-
 Neoteny
Neoteny
-
 Radical
Radical
-
 Extrasolar
Extrasolar
-
 Cotylopus acutipinnis
Cotylopus acutipinnis
-
 NAO
NAO
-
 Parallax
Parallax
-
 Grading
Grading
-
 Protandrous
Protandrous
-
 Eczema
Eczema
-
 Critical temperature
Critical temperature
-
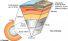 Mantle
Mantle
-
 Fasciculation
Fasciculation
-
 Scarring
Scarring
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) was founded in 1970, under the direction of the Department of Commerce. The NOAA provides and ensures access in suitable time to world environmental data and information services from satellites and other sources with the aim of promoting, protecting and improving the economy, the security, the environment and the quality of life of the nation.
This mission includes the protection of life and property against natural and technological hazards, with an emphasis on forecasting, preparation, reaction, re-establishment and mitigation measures.
The NOAA uses two satellite systems: polar orbit environmental satellites (POES) and geostationary orbit environmental satellites (GOES). The data from these satellites, and from others not belonging to the NOAA, is used to provide operational products on a continuous basis. Many of these products are used to support natural disaster management of tropical cyclones and other storms, flooding, drought, clouds of volcanic dust threatening aviation, sea ice and icebergs that are a hazard to sea navigation, coastal hazards and solar flares.
Satellites not belonging to the NOAA but used by it include the satellites in the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP), other geostationary satellites, QuickSCAT and the Total Ozone Monitor Satellite (TOMS) belonging to the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA), RADARSAT-1 belonging to the ASC and ERS-2 belonging to the ESA. The NOAA also uses data from commercial satellites.
The NOAA has several departments, each one specialised in a particular task:
- The National Ocean Service studies the oceans;
- The National Weather Service makes weather forecasts;
- The Satellite and Information Service, is in charge of the fleet of weather satellites;
- The NOAA Fisheries Service studies marine resources and promotes the conservation of ecosystems;
- The research department;
- The Office of Marine and Aviation Operations manages the agency's fleet of weather ships and aircraft.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



