-
 Weighted digital code
Weighted digital code
-
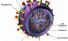 Influenza
Influenza
-
 Defecation
Defecation
-
 Clausius postulate
Clausius postulate
-
 Hypocentre
Hypocentre
-
 Catalase
Catalase
-
 Die
Die
-
 Duplex
Duplex
-
 Enuresis
Enuresis
-
 Migratory
Migratory
-
 Extrasolar
Extrasolar
-
 Prompt
Prompt
-
 Polymerase
Polymerase
-
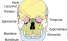 Cranium
Cranium
-
 Pioneer species
Pioneer species
-
 Phenytoin
Phenytoin
-
 Shiga toxin
Shiga toxin
-
 Asynchronous
Asynchronous
-
 Spawning ground
Spawning ground
-
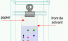 Chromatography
Chromatography
-
 STI
STI
-
 Osteoblast
Osteoblast
-
 Pneumatolytic
Pneumatolytic
-
 CD-V
CD-V
-
 Insectivore
Insectivore
-
 Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
-
 Mediterranean diet
Mediterranean diet
-
 Pterophile
Pterophile
-
 Beta version
Beta version
-
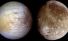 Io
Io
ESA
The ESA is theEuropean Space Agency. It is the equivalent in Europe of NASA in the USA
The European Space Agency is Europe's gateway to space. Its mission is to plan the development of European space capacity and ensure that European citizens continue to benefit from the investments made in the field of space.
The ESA has 19 Member States. By coordinating the financial and intellectual resources of its members, it can undertake programmes and activities that go well beyond what could be achieved by each country alone
What does the ESA do?
The ESA’s mission is to plan and carry out the European space programme. The agency's projects are designed to learn more about the Earth, its immediate environment in space, the solar system and the universe, and to develop satellite technologies and services to promote European industry. The ESA also works in close collaboration with space organisations outside Europe for the benefits of space to be shared by the whole of humanity.
Who belongs to the ESA?
The 19 ESA Member States are Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. In addition, Hungary, Poland, Slovenia and Estonia are European States cooperating with the ESA. Canada participates in some ESA projects under a cooperation agreement.
As can be seen from the list, not all European Union members are members of the ESA and not all the members of the ESA are members of the EU. The ESA is an entirely independent organisation, even though it maintains close relations with the EU in virtue of the framework agreement between the two organisations. The ESA and the EU share the same European space strategy and define a European space policy together
In 2011, its budget was 4 billion Euros. Considerably less than its sister organisation NASA.
 ESA
ESA
Latest
Fill out my online form.



