-
 Google Bombing
Google Bombing
-
 Cholera
Cholera
-
 Temperature
Temperature
-
 Hydrothermal circulation
Hydrothermal circulation
-
 Chickenpox
Chickenpox
-
 Adware
Adware
-
 Craton
Craton
-
 Resorption
Resorption
-
 Auricles
Auricles
-
 Hermaphrodite
Hermaphrodite
-
 American foulbrood
American foulbrood
-
 Game reserve
Game reserve
-
 Convention on Biological Diversity
Convention on Biological Diversity
-
 Class II antiarrhythmics
Class II antiarrhythmics
-
 Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam
-
 Drone
Drone
-
 Bud break
Bud break
-
 GNU
GNU
-
 Cloning
Cloning
-
 Moore's law
Moore's law
-
 IOPC Funds
IOPC Funds
-
 HDMI
HDMI
-
 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
-
 Certificate
Certificate
-
 Dementia
Dementia
-
 Microblogging
Microblogging
-
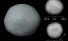 Pallas
Pallas
-
 Irradiation
Irradiation
-
 Salting out
Salting out
-
 Chemical graining
Chemical graining
Bayer name
The Bayer name is the combination of a Greek letter and the name of a constellation (Alpha Centauri, Epsilon Orionis etc.), used to identify bright stars. This notation was first used by Johan Bayer in 1603. The brightest star in a constellation usually bears the letter Alpha, the next brightest star Beta and so on. Some dim stars have names composed of a lower case letter of the Latin alphabet from a to z or upper case from A to Q (p Eridani, N Velorum etc.) See also Flamsteed number.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



