-
 Ecodriving
Ecodriving
-
 Contrast
Contrast
-
 Domestication
Domestication
-
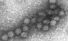 West Nile Virus
West Nile Virus
-
 Hololecratic
Hololecratic
-
 Endoreduplication
Endoreduplication
-
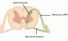 Interneurone
Interneurone
-
 Pyrophyllite
Pyrophyllite
-
 Atrophy
Atrophy
-
 Medullary
Medullary
-
 Huygens probe
Huygens probe
-
 Hercules globular cluster
Hercules globular cluster
-
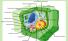 Peroxisome
Peroxisome
-
 Gabbro
Gabbro
-
 Lithification
Lithification
-
 Porphyroblast
Porphyroblast
-
 Cirrostratus cloud
Cirrostratus cloud
-
 Calvin cycle
Calvin cycle
-
 CD-I
CD-I
-
 Engine torque
Engine torque
-
 Catalytic site
Catalytic site
-
 Pathogenicity
Pathogenicity
-
 Triple DES
Triple DES
-
 Spring equinox
Spring equinox
-
 Spreadsheet
Spreadsheet
-
 Equatorial coordinates of a direction
Equatorial coordinates of a direction
-
 Proterozoic era
Proterozoic era
-
 Virtual reality
Virtual reality
-
 Tidal bore
Tidal bore
-
 Pistil
Pistil
Sewage sludge
Sewage sludge is residue from the treatment of liquid effluents by treatment plants. This sludge is composed of organic and mineral matter.
Sewage sludge is characterised by the amount of dry matter and organic matter it contains. These two parameters depend on how effluents are treated.
Different types of sewage sludge
There are different types of sludge, depending on the nature of the treatment process:
- primary sludge is the result of the settling of effluents. It generally contains a high amount of mineral matter;
- physical-chemical sludge is close to primary sludge but contains more of certain types of flocculated products;
- biological sludge is the product of the bacterial treatment of effluents. It is rich in organic matter.
Use of sewage sludge
This type of waste can be spread on farm land as a fertilising amendment, used by methanisation with the production of biogas, used in composting or incineration with cogeneration.
Depending on its intended use, sludge can be subjected to different types of treatment to reduce its water content, stabilise and stop its fermentation and reduce the risks of biological contamination.
If the available infrastructure or the characteristics of the sludge do not make this type of use possible, it is placed in storage centres.
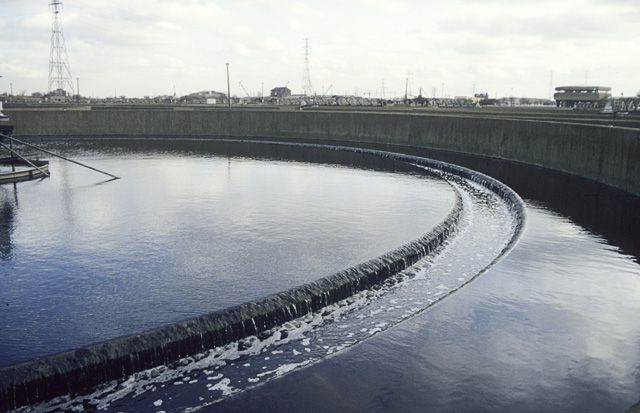 Sewage treatment producing biological sludge. © John Rostron, Geograph CC by-sa 2.0
Sewage treatment producing biological sludge. © John Rostron, Geograph CC by-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



