-
 Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
-
 Joint venture
Joint venture
-
 Koch Bacillus
Koch Bacillus
-
 Pauli exclusion principle
Pauli exclusion principle
-
 Parsnip
Parsnip
-
 Meningioma
Meningioma
-
 Neanderthal
Neanderthal
-
 Circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
-
 Henry
Henry
-
 Stalagmite
Stalagmite
-
 Gait
Gait
-
 OPEC
OPEC
-
 ATV
ATV
-
 Le Chatelier's principle
Le Chatelier's principle
-
 Ng, Np, Nm
Ng, Np, Nm
-
 Crystal lattice
Crystal lattice
-
 Wave velocity
Wave velocity
-
 Expansion valve
Expansion valve
-
 Nucleolus
Nucleolus
-
 Higgs boson
Higgs boson
-
 Polyamide
Polyamide
-
 Refrigerant fluid
Refrigerant fluid
-
 Coverts
Coverts
-
 Hysterography
Hysterography
-
 Chardonnay
Chardonnay
-
 URL
URL
-
 Freshwater
Freshwater
-
 Crystal growth
Crystal growth
-
 American Bullfrog
American Bullfrog
-
 Giant star
Giant star
Ramsar Convention
The Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat, or more simply the Ramsar Convention, is an international treaty on the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands.
Adopted in 1972 in the city of Ramsar, Iran (hence its name), this convention requires its members, including France, to:
- consider wetlands in the development and use of their territory;
- identify important wetlands, add them to the Ramsar list and ensure their conservation;
- preserve all wetlands;
- cooperate with neighbouring countries in the conservation of cross-border wetlands.
This convention also provided a wide definition of what may be considered a wetland, i.e. all "areas of marshes, fen [Note: swampy moors of the Ardennes plateaus], peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt water, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres".
In 2009 over 1,800 of these areas were included on the Ramsar list for an area of over 1.6 million hectares, even though these areas are still subject to as much pressure as they were in 1972.
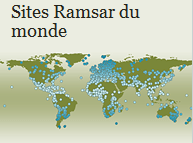
Location of wetlands listed in the Ramsar Convention from around the world. © Ramsar Convention
Latest
Fill out my online form.



