-
 Moquette Tanne
Moquette Tanne
-
 Sex glands
Sex glands
-
 Server
Server
-
 Exhalative deposit
Exhalative deposit
-
 Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine
-
 Cholinergic
Cholinergic
-
 Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris
-
 Sebkha
Sebkha
-
 Freeware
Freeware
-
 Colony
Colony
-
 Puddingstone
Puddingstone
-
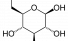 Glucose
Glucose
-
 Private key
Private key
-
 Solute
Solute
-
 Melanism
Melanism
-
 Scraping
Scraping
-
 Sauropoda
Sauropoda
-
 Gestation
Gestation
-
 Comet tail
Comet tail
-
 Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenoma
-
 Ribonucleotide
Ribonucleotide
-
 RFC
RFC
-
 Transplantation
Transplantation
-
 Pleistocene
Pleistocene
-
 Salix viminalis
Salix viminalis
-
 Fishing reserve
Fishing reserve
-
 White noise
White noise
-
 GPU
GPU
-
 Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis
-
 Endocytosis
Endocytosis
Hazardous waste
Hazardous waste is waste that, due to its composition or properties, poses a threat to human health or to the environment.
This type of waste must undergo a series of specific processes in order to reduce toxicity and the risk of contamination. Hazardous waste therefore requires specific collection, transportation, treatment, recycling and disposal procedures.
Different types of hazardous waste
There are different types of hazardous waste defined by origin:
- hazardous household waste (HHW) is produced by households, and includes aerosols, gardening products, DIY products, mercury thermometers, etc.;
- hazardous industrial waste (HIW) produced by heavy industry and businesses, such as clinker , sewage sludge, solvents, phytosanitary waste, etc.;
- medical waste that poses a risk of infection and assimilated waste (in France, this is referred to by the acronym 'DASRIA'). Medical waste is produced by hospitals and veterinary centres, and includes items such as syringes, cultures, anatomical fragments, dressings, etc.
In France there is a plan to manage all of this type of waste:the regional dangerous waste elimination plan (PREDD).
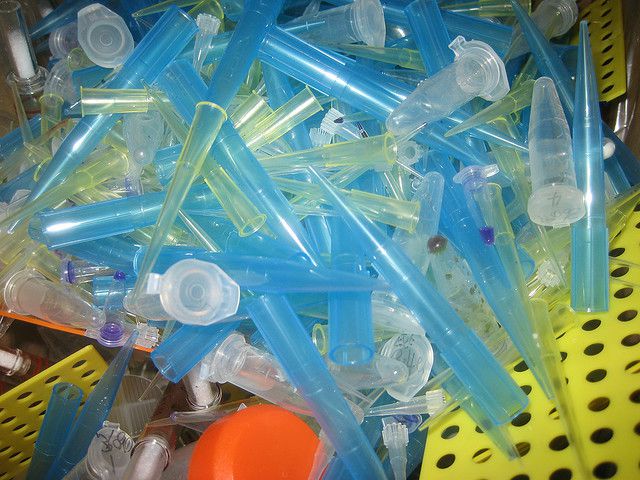 Medical analysis laboratories produce a large amount of waste that has a risk of infection. This waste must be subjected to specialised treatment. © Simon Li CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Medical analysis laboratories produce a large amount of waste that has a risk of infection. This waste must be subjected to specialised treatment. © Simon Li CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



