-
 MBMS
MBMS
-
 Acne
Acne
-
 Feral
Feral
-
 Biofuel
Biofuel
-
 Phenotype
Phenotype
-
 TDMA
TDMA
-
 Internal combustion hydrogen engine
Internal combustion hydrogen engine
-
 Gunning
Gunning
-
 Dengue fever virus
Dengue fever virus
-
 Expectorate
Expectorate
-
 Song
Song
-
 Stimulated emission
Stimulated emission
-
 Sodolithic
Sodolithic
-
 Invasive
Invasive
-
 Extinction
Extinction
-
 Fentes alpines
Fentes alpines
-
 Cementite
Cementite
-
 Neovascularisation
Neovascularisation
-
 Blob
Blob
-
 Noise
Noise
-
 Microfluidics
Microfluidics
-
 Nucleon
Nucleon
-
 DRCS
DRCS
-
 Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics
-
 Monsoon
Monsoon
-
 Lambda phage
Lambda phage
-
 Crop
Crop
-
 Proof
Proof
-
 Hurricane
Hurricane
-
 Angelica
Angelica
Down quark
The down quark is a particle of matter. It is one of the six quarks in the standard model and is considered to be an elementary particle in our current state of knowledge.
The down quark is one of the six quarks, the others being :
- the up quark;
- the top quark;
- the bottom quark;
- the charm quark;
- the strange quark.
The down quark
Like its companions it is a fermion; it has a fractional electrical charge equal to -1/3 e. It is one of the first three quarks postulated at the beginning of the 1960s independently by Gell-Mann, Yuval Ne'eman and George Zweig to understand and classify the hadrons that were known at the time.

Two of the discoverers of quark theory. © universe-review
Currently it is part of what is called the first generation of particles in the standard model, where, with the up quark, it forms the nucleons. The proton therefore contains one down quark and two up quarks, while the neutron contains two down quarks and one up quark bound together by the strong nuclear interactions described in quantum chromodynamics.
The existence of the d quark only started being accepted in the 1960s and especially the beginning of the 1970s when the theory of quark confinement partially explained why quarks were never observed free, but only inside hadrons.
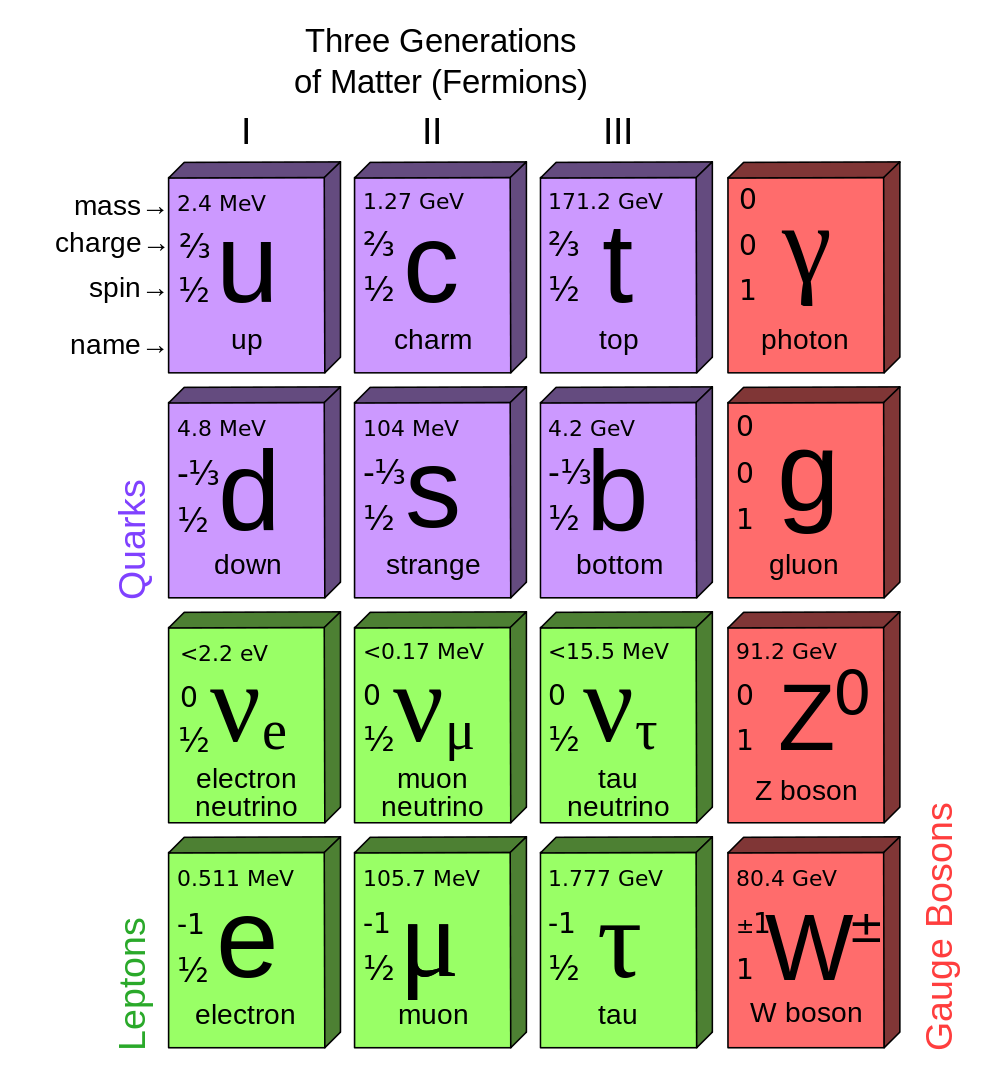 The table of elementary particles in the standard model which includes the down quark. © MissMJ, Wikipedia
The table of elementary particles in the standard model which includes the down quark. © MissMJ, Wikipedia
Latest
Fill out my online form.



