-
 Colloid
Colloid
-
 Acinar
Acinar
-
 Orbitography
Orbitography
-
 Hash function
Hash function
-
 Osterrite
Osterrite
-
 Magnetoresistance
Magnetoresistance
-
 Conveyor belt
Conveyor belt
-
 Tubal ligation
Tubal ligation
-
 Larva
Larva
-
 Bioenergy
Bioenergy
-
 Maritime swamp
Maritime swamp
-
 Truncation
Truncation
-
 TCP/IP
TCP/IP
-
 Arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension
-
 Atherogenic
Atherogenic
-
 European black pine
European black pine
-
 IAM
IAM
-
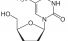 Thymidine
Thymidine
-
 iPod Nano
iPod Nano
-
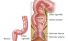 Rectum
Rectum
-
 Microglia
Microglia
-
 Phenytoin
Phenytoin
-
 Ebb
Ebb
-
 Guava
Guava
-
 Angiotensin
Angiotensin
-
 Calamus
Calamus
-
 Package
Package
-
 Oxidase
Oxidase
-
 Deuterostome
Deuterostome
-
 Dielectric
Dielectric
Bergeron Effect
The Bergeron process is a mechanism that causes the formation of precipitations of many hydrometeors (rain, snow, hail, etc.).
In the area under the freezing point of a cloud, water exists in its three phases: gaseous (vapour), liquid (supercooled) and solid (ice crystal).
Principle of the Bergeron effect
The Bergeron effect is the continuous transfer of water vapour from supercooled droplets to ice crystals. This is due to the difference in relative humidity around the supercooled water and the ice: the humidity level is higher near the droplets than it is near the ice crystals.
Therefore water vapour diffuses towards the ice crystals, which become larger at the expense of the droplets. Their weight increases until it causes them to fall. A second phenomenon, coalescence, then comes into play to continue increasing the weight of the hydrometeors, leading to their precipitation.
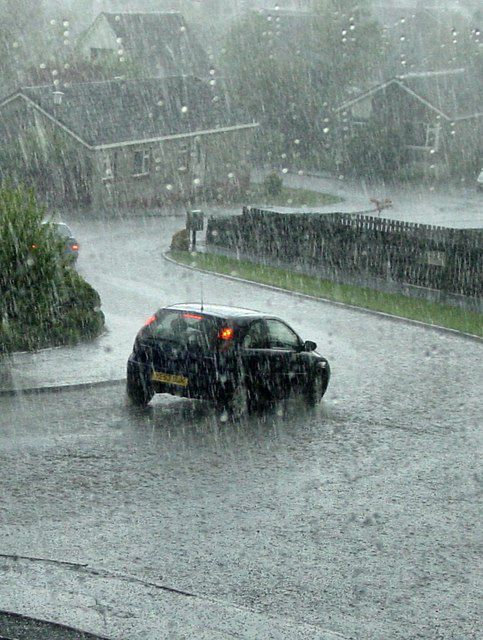 The Bergeron process causes rain. © Iain Farquhar, Geograph CC by-sa 2.0
The Bergeron process causes rain. © Iain Farquhar, Geograph CC by-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



