-
 Internal tide
Internal tide
-
 Electric shock
Electric shock
-
 Pangea
Pangea
-
 Hyoid
Hyoid
-
 Cline
Cline
-
 CERT
CERT
-
 Free-electron laser
Free-electron laser
-
 Auto-immune diseases
Auto-immune diseases
-
 Wind turbine
Wind turbine
-
 Oscillograph
Oscillograph
-
 Expectorant
Expectorant
-
 Precession constant
Precession constant
-
 Plug-in
Plug-in
-
 Triton
Triton
-
 Constellation of Scorpio
Constellation of Scorpio
-
 Hubble constant
Hubble constant
-
 Galileo
Galileo
-
 xDSL
xDSL
-
 Eutrophication
Eutrophication
-
 GSM
GSM
-
 Datagram
Datagram
-
 Neoteny
Neoteny
-
 Shergottite
Shergottite
-
 Viral load
Viral load
-
 Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen cycle
-
 Hepatitis
Hepatitis
-
 Annual parallax
Annual parallax
-
 Monoethanolamine
Monoethanolamine
-
 Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency
-
 Truncation
Truncation
Yersin bacillus
The Yersin bacillus (or Yersinia pestis) is the pathogenic agent responsible for the plaque.
Characteristics of the Yersin bacillus
This rod-shaped Enterobacteriaceae is a Gram negative bacterium. It was discovered on 20 June 1894, by Yersin, a Swiss physician. It is now classified as a bio-terrorism agent A.
Two strains of Yersinia pestis (KIM and CO92) have been completely sequenced. Their respective chromosomes are more than 4.6 million base pairs longs. They also contain three plasmids, two of which are essential for their transmission by fleas.
Yersin bacillus and the plague
The Yersin bacillus belongs to the Yersiniagenus and is transmitted by fleas whereas the only other two bacteria in the genus (Y. Enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis) which are known to be pathogenic to human beings are transmitted faeco-orally. The bacterium can therefore be transmitted by rats to human beings via fleas.
A bite from the infected flea leads to the bacteria being introduced through the skin towards the lymphatic system. After multiplying in a lymph node the bacteria reached the blood circulation and are distributed throughout the body.
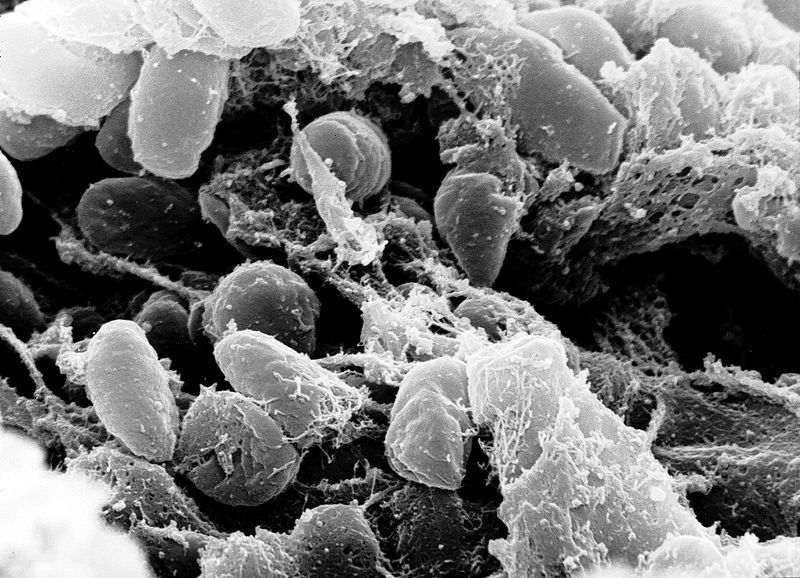 The agent responsible for the plaque is a bacterium called Yersinia pestis. © DR
The agent responsible for the plaque is a bacterium called Yersinia pestis. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



