-
 Gamma globulin
Gamma globulin
-
 Bearded seal
Bearded seal
-
 Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
-
 Air conditioning
Air conditioning
-
 Basil
Basil
-
 Perigee
Perigee
-
 Crystal face
Crystal face
-
 Desertification
Desertification
-
 Soyuz
Soyuz
-
 CRT
CRT
-
 Byssus
Byssus
-
 Carbene
Carbene
-
 Ecodriving
Ecodriving
-
 Chimeric genome
Chimeric genome
-
 Azimuthal mount
Azimuthal mount
-
 ITER
ITER
-
 Nail
Nail
-
 ASIC
ASIC
-
 Aponeurosis
Aponeurosis
-
 Tropical year
Tropical year
-
 Dyspnoea
Dyspnoea
-
 Storable propellant stage.
Storable propellant stage.
-
 TNM Classification
TNM Classification
-
 NEAR-Shoemaker
NEAR-Shoemaker
-
 Mars Odyssey
Mars Odyssey
-
 Biotope
Biotope
-
 Variability in heart rate
Variability in heart rate
-
 Ovipositor
Ovipositor
-
 Exoskeleton
Exoskeleton
-
 Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 21, also called Downs syndrome, is a specific trisomy involving chromosome 21. It is one of the rare trisomies which is consistent with pregnancy being continued to term.
Consequences of trisomy 21
The child, however, has typical symptoms:
- a specific morphology (facies, short height) ;
- organ and joint malformations;
- and mental retardation which, however, does not often prevent social integration.
Although the clinical signs are well known the diagnosis is only made by performing a karyotype (analysis of the number of chromosomes in a cell).
Free trisomy and translocation trisomy
There are two forms of trisomy 21 : free trisomy and translocation trisomy.
- Free trisomy may arise from a gamete (ovum or spermatozoon) Incorrectly containing 24 chromosomes instead of 23. If all of the cells have 47 chromosomes, the term homogeneous trisomy 21 is used. If the cells have 46 chromosomes the term trisomy mosaic is used;
- Translocation trisomy 21 is rarer and involves the attachment of the third chromosome 21 to another chromosome. In this case there is a total of 46 chromosomes but in reality the genetic material of chromosome 21 is carried three times.
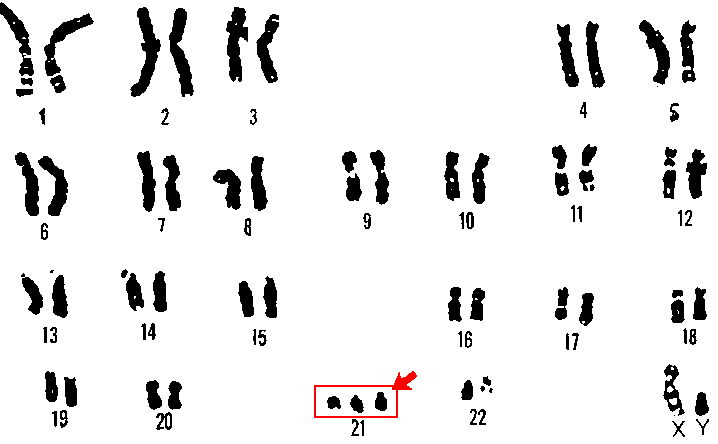 The karyotype of a trisomy 21 person often has 47 chromosomes (3 chromosomes 21), but occasionally has 46 in translocation trisomy. © DR
The karyotype of a trisomy 21 person often has 47 chromosomes (3 chromosomes 21), but occasionally has 46 in translocation trisomy. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



