-
 Chorea
Chorea
-
 Basic rock
Basic rock
-
 MBR
MBR
-
 HLA
HLA
-
 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
-
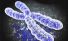 Haplotype
Haplotype
-
 Mitosis
Mitosis
-
 Quantum cryptography
Quantum cryptography
-
 Inclusion
Inclusion
-
 Gabapentin
Gabapentin
-
 Computer worm
Computer worm
-
 Orbit
Orbit
-
 Heliopause
Heliopause
-
 Turner's Syndrome
Turner's Syndrome
-
 Genotype
Genotype
-
 Agglutination
Agglutination
-
 Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
-
 Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy
-
 Calculus
Calculus
-
 Marpol Convention
Marpol Convention
-
 Graphite
Graphite
-
 Minamata Bay Disaster
Minamata Bay Disaster
-
 Eruptive
Eruptive
-
 Cell reprogramming
Cell reprogramming
-
 Valine
Valine
-
 EUMETSAT
EUMETSAT
-
 Homochromy
Homochromy
-
 GNU
GNU
-
 EFSA
EFSA
-
 CP symmetry violation
CP symmetry violation
Thrombosis
A thrombosis is a blood clot which forms in a vein (venous thrombosis) or artery (arterial thrombosis). The blood coagulates when circulating blood is slowed by immobilisation of a limb (leg) or by an obstruction (atheroma).
Consequences of thrombosis
Venous thrombosis may cause phlebitis, obstruction of the venous circulation resulting in pain, local warmth, and swelling of the leg.
Arterial thrombosis may ultimately obstruct the artery and cause ischaemia.
Embolism
In both situations, detachment of the clot and its transport through the blood circulation to other organs is called embolism. The clot then blocks the circulation in organs such as the lung (pulmonary embolism) or the brain (CVA), and can also lead to myocardial infarction.
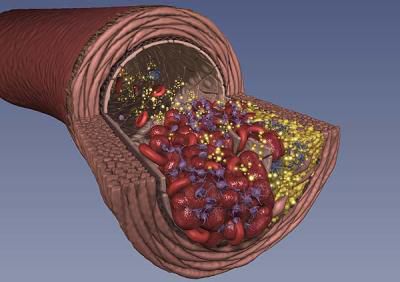 Thrombosis can be venous or arterial. © DR
Thrombosis can be venous or arterial. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



