-
 Hydrazine
Hydrazine
-
 VOD
VOD
-
 RFC
RFC
-
 Akari
Akari
-
 Symbian
Symbian
-
 Dolby Digital 5.1
Dolby Digital 5.1
-
 Acusia
Acusia
-
 Certificate
Certificate
-
 Spin
Spin
-
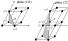 Haüy indices
Haüy indices
-
 Xylophagy
Xylophagy
-
 Parasol
Parasol
-
 Pink siris
Pink siris
-
 Vaginal examination
Vaginal examination
-
 Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia
-
 Chronic
Chronic
-
 Dengue fever
Dengue fever
-
 Lyme's Disease
Lyme's Disease
-
 Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin
-
 Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
-
 Hydroelectric pumping station
Hydroelectric pumping station
-
 Drainage
Drainage
-
 Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation
-
 Swell
Swell
-
 svRNA
svRNA
-
 Lentiginosis
Lentiginosis
-
 Scapula
Scapula
-
 Homolysis
Homolysis
-
 Canopy
Canopy
-
 Osteoblast
Osteoblast
systemic antifungals
The systemic antifungals are used when the organism responsible – a microscopic fungus - is resistant or if local treatment is impossible. This applies to widespread infections, recurring local infections such as some genital infections in women - specific sites (particularly gastro-intestinal tract) or in a context of immunosuppression.
How do the systemic antifungals work?
The systemic antifungals are administered as tablets or by injection. Like the topical antifungals these medicines can be fungistatic - in other words they inhibit or slow multiplication of the fungus - or fungicides. In this case they kill the fungi. An antifungal can act as different levels in the fungus.
Do they have contraindications or precautions?
Known allergy to the medicine, pregnancy or breast-feeding, some therapeutic combinations, known hepatic, cardiac or rental impairment are all major contraindications. In terms of side effects, the most commonly reported are liver function abnormalities, gastro-intestinal and visual problems and skin rashes.
Source Interview with Dr Nina Roos, Dermatologist in Paris, 20 June 2011
 Orally, when topical treatment is ineffective. © Phovoir
Orally, when topical treatment is ineffective. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



