-
 Shuttering blocks
Shuttering blocks
-
 Morning-after pill
Morning-after pill
-
 Diapedesis
Diapedesis
-
 PCI Express
PCI Express
-
 Astrophysics
Astrophysics
-
 Fuel oil
Fuel oil
-
 DRM
DRM
-
 Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis
-
 Heliopause
Heliopause
-
 Pyroclastic surge
Pyroclastic surge
-
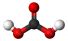 Carbonic acid
Carbonic acid
-
 Palomares nuclear incident
Palomares nuclear incident
-
 Group
Group
-
 Adenoma
Adenoma
-
 Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic
-
 Data stream encryption
Data stream encryption
-
 Obliquity
Obliquity
-
 Haploidy
Haploidy
-
 Hominoidea
Hominoidea
-
 New Technology Telescope
New Technology Telescope
-
 Suborbital
Suborbital
-
 M16
M16
-
 Leukopenia
Leukopenia
-
 CNG
CNG
-
 Moon
Moon
-
 Darwin
Darwin
-
 Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemia
-
 Unix
Unix
-
 Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
-
 Asparagus
Asparagus
Syphilis
Syphilis is bacterial infection caused by a sexually transmissible pathogenic agent (Treponema pallidum).
Transmission of syphilis
Syphilis is transmitted during sexual relations (oral, genital, or anal) with an infected partner. A pregnant woman with syphilis can transmit the infection to the foetus, which sometimes causes congenital abnormalities or even foetal death. Syphilis can also be transmitted by sharing syringes or from a skin lesion, although this is rare.
Symptoms of syphilis
Primary syphilis is characterised by a painless sore at the primary infection site (genitals, mouth, etc.) where the bacterium begins to multiply. After this initial sore (or chancre) has healed, which may take several weeks, a rash develops over the entire body.
If it is not treated, syphilis can become secondary (flu-like symptoms, jaundice, meningitis), or even tertiary (chronic, with internal organ damage) and cause the death of the patient.
Treatment of syphilis
Syphilis can be diagnosed by a simple blood test and is easily treated by penicillin or other antibiotics.
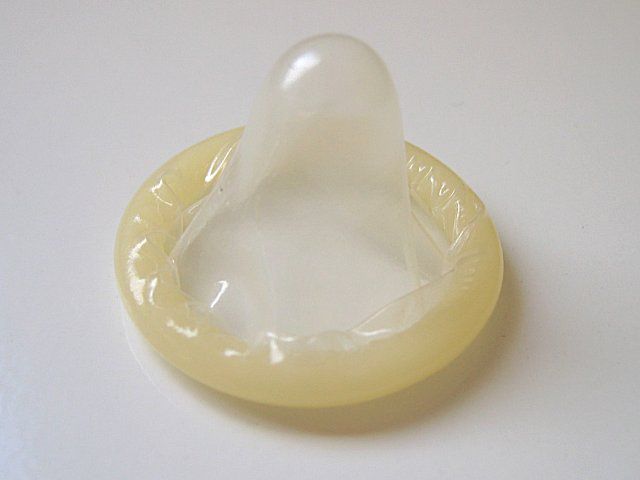 Syphilis is a sexually transmissible disease that can be avoided by wearing a condom. © DR
Syphilis is a sexually transmissible disease that can be avoided by wearing a condom. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



