-
 Liver fluke
Liver fluke
-
 Epidemic
Epidemic
-
 Backing block
Backing block
-
 Extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix
-
 Soyuz-Ikar
Soyuz-Ikar
-
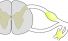 Nerve root
Nerve root
-
 Conventional cytotoxic medicine
Conventional cytotoxic medicine
-
 Micturition
Micturition
-
 Aleppo pine
Aleppo pine
-
 Embossing
Embossing
-
 Phytochrome
Phytochrome
-
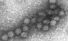 West Nile Virus
West Nile Virus
-
 Proteus
Proteus
-
 Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology
-
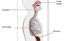 Oesophagus
Oesophagus
-
 WAP
WAP
-
 Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance
-
 Olivine
Olivine
-
 antiarrhythmics
antiarrhythmics
-
 Conduction band
Conduction band
-
 Contraceptive vaginal ring
Contraceptive vaginal ring
-
 iTunes
iTunes
-
 Heterozygote
Heterozygote
-
 Mammal
Mammal
-
 Antivenom
Antivenom
-
 Vaginal douche
Vaginal douche
-
 Hackberry
Hackberry
-
 Wading bird
Wading bird
-
 Asian black bear
Asian black bear
-
 Zodiacal light
Zodiacal light
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a pathogenic bacterium in human beings.
Features of Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the Staphylococcus genus and is a Gram positive bacterium which is a coccus, and forms clusters (raisin bunches) or chains. The bacterial cell is approximately 1 micrometre in diameter and is immobile.
The genome is contained on a chromosome of approximately 2.8 million base pairs which code 2,700 proteins.
Staphylococcus aureus and infections
Although it is often found in human beings, it does not always cause infection. It can cause skin infections (boils, folliculitis, whitlow, impetigo etc) or mucosal infections (otitis, conjunctivitis, etc.) which may result in septicaemia. It also causes nosocomial infections, food poisoning and its antibiotic resistance is occasionally a major problem in treating patients.
Staphylococcus aureus produces various toxins: haemolysins, leukocidin, enterotoxins, Staphylococcal toxic shock toxin or TSST-1 (temperature over 39°C, hypotension, erythroderma, which is fatal in 10% of patients), and exfoliatins.
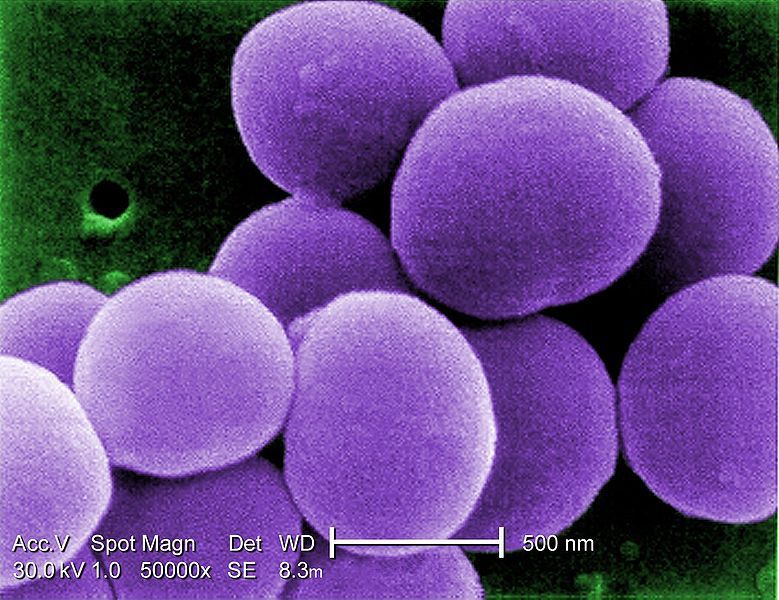 Staphylococcus aureus is a pathogenic bacterium to human beings. © DR
Staphylococcus aureus is a pathogenic bacterium to human beings. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



