-
 Repeater
Repeater
-
 Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids
-
 Iliac crest
Iliac crest
-
 Hydroponics
Hydroponics
-
 Total suspended solids
Total suspended solids
-
 Molecular hybridisation
Molecular hybridisation
-
 Residual error rate
Residual error rate
-
 Graben
Graben
-
 Rabbit fever
Rabbit fever
-
 GUT
GUT
-
 Noctilucent cloud
Noctilucent cloud
-
 Electromyogram
Electromyogram
-
 Stereochemical formula
Stereochemical formula
-
 Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine
-
 Uranium
Uranium
-
 Heisenberg inequalities
Heisenberg inequalities
-
 Tungsten
Tungsten
-
 Metasomatose
Metasomatose
-
 Isthmus
Isthmus
-
 Layering
Layering
-
 Anaesthetise
Anaesthetise
-
 Barycentric
Barycentric
-
 Plasmid
Plasmid
-
 Pharynx
Pharynx
-
 Osmosis
Osmosis
-
 Curative
Curative
-
 Anseriformes
Anseriformes
-
 Spermicide
Spermicide
-
 Conductivity
Conductivity
-
 Extranet
Extranet
Septicaemia
Septicaemia is a generalised infection in the body caused by pathogenic bacterial micro-orgasms.
Causes of septicaemia
Septicaemia develops following an untreated or incorrectly treated primary infection. Bacteria are released regularly into the blood from a focus of infection which may be in the tooth, vein, uterus, urinary tract, heart or lung.
Symptoms of septicaemia
Septicaemia is defined when a bacterial infection is found in blood (bacteraemia) and some of the following symptoms are present:
- temperature over 38°C or under 36°C;
- tachycardia;
- severe fall in blood pressure;
- high respiratory rate (over 20 per minute);
- fatigue.
Risks of septicaemia
Untreated, septicaemia may lead to secondary foci of infection. Septicaemia may progress to septic shock involving a sudden severe fall in blood pressure, shivering and tachycardia. 40 - 50% of these cases are then fatal.
Treatment of septicaemia
Antibiotics are required to kill or prevent the spread of bacteria. A broad spectrum antibiotic is used initially and after microbiological tests, the most appropriate specific antibiotic is identified.
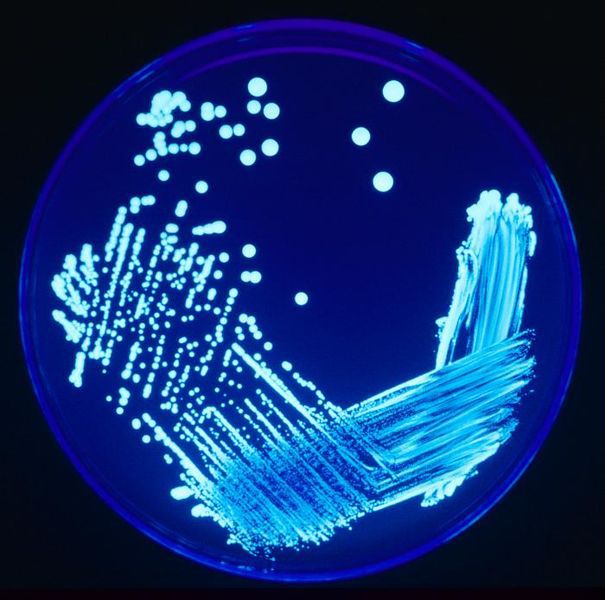 Septicaemia is a generalised bacterial infection of the blood. © DR
Septicaemia is a generalised bacterial infection of the blood. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



