-
 MD2
MD2
-
 Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
-
 Glycosidic bond
Glycosidic bond
-
 Poisson ratio
Poisson ratio
-
 Phenytoin
Phenytoin
-
 Prevention
Prevention
-
 E-book
E-book
-
 Olfactory centres
Olfactory centres
-
 White dwarf
White dwarf
-
 Herpes
Herpes
-
 Erenna
Erenna
-
 Bubonic plague
Bubonic plague
-
 Gauge fields
Gauge fields
-
 Legionella
Legionella
-
 Second
Second
-
 RIR
RIR
-
 Renaturation
Renaturation
-
 Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis
-
 Vaccine
Vaccine
-
 Pandiculation
Pandiculation
-
 Alkaloid
Alkaloid
-
 Cambium
Cambium
-
 Dormant
Dormant
-
 Constellation of Draco
Constellation of Draco
-
 CDP
CDP
-
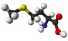 Methionine
Methionine
-
 Mixotrophy
Mixotrophy
-
 Burst
Burst
-
 Nicol
Nicol
-
 Trackpad
Trackpad
Proton pump inhibitor
The proton pump inhibitors (PPI) are used in the management of gastric and duodenal ulcers and more recently for gastro-oesophageal reflux (GOR). They are also used to treat the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, which is due to hypersecretion of gastrin by the stomach. Finally, they are widely prescribed in the prevention and management of peptic problems due to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID).
How to the PPI work?
The PPI inhibit the pump which produces acidity in the stomach (the proton pump) and therefore regulate the production of acid at its source. They are absorbed in the small intestine and block the acid secretion of cells in the stomach wall. They are generally administered as a single daily dose in the morning or evening as indicated. Morning and evening doses may be prescribed in a few specific situations.
Side effects and precautions
The PPI may cause gastro-intestinal problems, particularly constipation and diarrhoea. They can also cause headaches and much more rarely mental confusion or blood count abnormalities.
Sources:
- Merck Manuel 4th
- Pharmacorama edition, site accessed on 5 July 2011
 The PPI for gastro-œsophageal reflux. © Phovoir
The PPI for gastro-œsophageal reflux. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



