-
 Antacids
Antacids
-
 Linear dune
Linear dune
-
 Unknown
Unknown
-
 Pneumatolytic
Pneumatolytic
-
 Indicator species
Indicator species
-
 Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
-
 Graben
Graben
-
 Endoprosthesis
Endoprosthesis
-
 Ovary
Ovary
-
 Neutrino
Neutrino
-
 Olivine
Olivine
-
 Pesticide
Pesticide
-
 Spleen
Spleen
-
 Diatomite
Diatomite
-
 Surgery
Surgery
-
 Nucleon
Nucleon
-
 Sewage sludge
Sewage sludge
-
 Oesophagus
Oesophagus
-
 Subspecies
Subspecies
-
 Plasmid
Plasmid
-
 Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria
-
 Java
Java
-
 Reunion Island ornate day gecko
Reunion Island ornate day gecko
-
 Permafrost
Permafrost
-
 Bioenergy
Bioenergy
-
 Meconium
Meconium
-
 Heat transfer fluid
Heat transfer fluid
-
 Endemism
Endemism
-
 Compression
Compression
-
 Photovoltaic panel
Photovoltaic panel
Ovulation
Ovulation is the stage when an oocyte is released by the ovary. It occurs around the 14 or 15th day of the menstrual cycle in women.
Role of ovulation
The aim of ovulation is to release an ovule (or rather an oocyte as it has not finished its meiosis process) ready to be fertilised by a spermatozoon in the fallopian tubes and give birth to an embryo.
Hormonal regulation of ovulation
Ovulation is very finely regulated by sex hormones. FSH, which is produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates growth of follicles in the ovaries in which the ovules are found. An LH peak also produced by the pituitary gland induces ovulation in the next 36 to 48 hours. FSH also contributes to ovulation as it makes the wall of the ovary fragile allowing the ovule to enter the Fallopian tubes.
Symptoms of ovulation
The time of ovulation can be identified from a body temperature curve. In addition, the cervical mucus (the mucus which protects the vagina from infections) also changes appearance to enable the sperm to reach the fallopian tubes more easily. It can be collected from the cervix and its consistency can be analysed. The period of ovulation is indicated if it is clear and can be stretched between two fingers without breaking.
Ovulation and menopause
Ovarian activity ceases during menopause, at around 50 years of age so ovulation and menstrual period no longer occur and the woman becomes infertile and can no longer have children. However, she can continue to have a normal sex life.
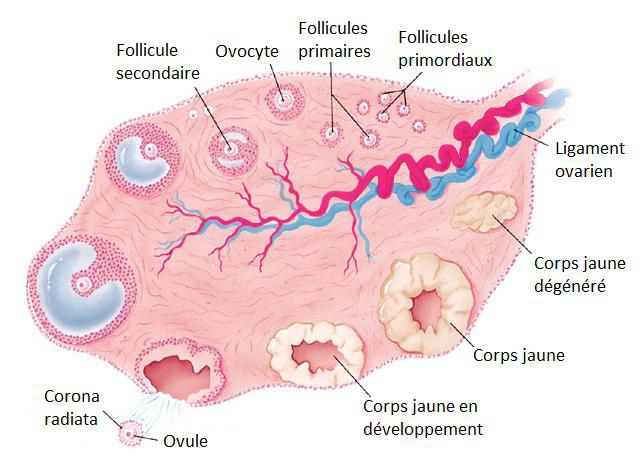 Ovulation takes place in the ovary. © DR
Ovulation takes place in the ovary. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



