-
 Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
-
 Tanne inclusion
Tanne inclusion
-
 Urushiol
Urushiol
-
 Magnetic permeability
Magnetic permeability
-
 Metapleural gland
Metapleural gland
-
 Nematocyte
Nematocyte
-
 E-book
E-book
-
 Differentiation
Differentiation
-
 White noise
White noise
-
 Optical doublet
Optical doublet
-
 Third law of thermodynamics
Third law of thermodynamics
-
 Ecological continuum
Ecological continuum
-
 Self-signed key
Self-signed key
-
 Nozzle
Nozzle
-
 Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts
-
 PC
PC
-
 Engine torque
Engine torque
-
 Regulus
Regulus
-
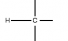 Methylation
Methylation
-
 Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis
-
 Cytochrome
Cytochrome
-
 Extension bus
Extension bus
-
 Piezometer
Piezometer
-
 Obliquity
Obliquity
-
 Dysaesthesia
Dysaesthesia
-
 Be star
Be star
-
 Air braking
Air braking
-
 Paleozoic
Paleozoic
-
 Pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
-
 Papillary angioma
Papillary angioma
Outer ear
As its name indicates the outer ear is the outermost part of the auditory system.
Structure of the outer ear
The outer ear is both a protective and resonance structure and is made up of the pinna (or auricular shell) and the auditory canal which leads to the tympanic membrane.
Role of the outer ear
The pinna captures and concentrates sound waves while buffering sudden transfer of open air into the enclosed air in the auditory canal. These acoustic waves then pass along the auditory canal behaving as rectilinear waves over approximately 2 to 3 centimetres before encountering the tympanic membrane. This then oscillates in response to fluctuations in the acoustic wave in the canal.
Functioning of audition. © ide.fr
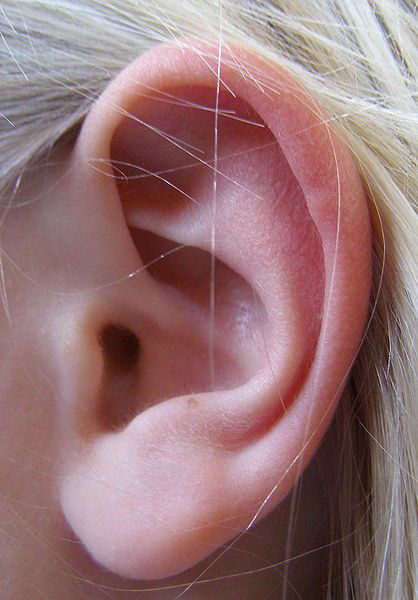 The outer ear is the most visible part of the ear. © DR
The outer ear is the most visible part of the ear. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



