-
 Autologous transplantation
Autologous transplantation
-
 Cytokinin
Cytokinin
-
 Salt gland
Salt gland
-
 GFP
GFP
-
 Perl
Perl
-
 Protease inhibitor
Protease inhibitor
-
 Constipation
Constipation
-
 Meningitis
Meningitis
-
 Achromatopsia
Achromatopsia
-
 Condensation boiler
Condensation boiler
-
 Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
-
 Cranium
Cranium
-
 Mucosa
Mucosa
-
 Elongated facies
Elongated facies
-
 Amine acid group
Amine acid group
-
 Biomass
Biomass
-
 SEPP
SEPP
-
 Haemagglutinin
Haemagglutinin
-
 Limestone pavement
Limestone pavement
-
 Hydrology
Hydrology
-
 Convex
Convex
-
 Solenodon
Solenodon
-
 Expansion valve
Expansion valve
-
 Downsizing
Downsizing
-
 Apricot
Apricot
-
 Space-time
Space-time
-
 Laser
Laser
-
 Function
Function
-
 Diffraction
Diffraction
-
 Proton pump inhibitor
Proton pump inhibitor
Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (Acb) is part of the striato-pallido-thalamo-cortical loop although it also collects a large amount of information from other limbic structures including the BlA, hippocampus and pre-frontal cortex. It plays a central role in the brain reward circuit and consequently in the drug dependency process.
Its function relies on two main neurotransmitters, dopamine, which is an amplifier of desire and pleasure, and serotonin that produces feelings of inhibition and satiety.
It has been shown experimentally in human beings that all drugs without exception significantly increase the production of dopamine in the nucleus accubens while reducing production of serotonin at the same time. This involves progressive adaptation in the reward circuit which is partly inhibited by repeated use of drugs.
This leads to the tolerance phenomenon leading to increased doses of the drug being needed to experience the same effect as during the previous dose.
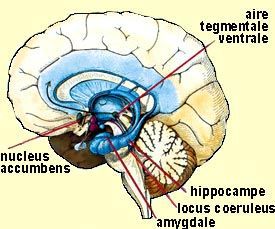
Position of the nucleus accubens in the human brain. Source unknown
Latest
Fill out my online form.



