-
 Insulin
Insulin
-
 Intumescent
Intumescent
-
 STD
STD
-
 Flood
Flood
-
 Selecting
Selecting
-
 Archean
Archean
-
 Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia
-
 Xylophagy
Xylophagy
-
 MERIS
MERIS
-
 Maritime pine
Maritime pine
-
 Frenulum
Frenulum
-
 Active galaxy nucleus
Active galaxy nucleus
-
 Pluto
Pluto
-
 Kiwi
Kiwi
-
 Riparian
Riparian
-
 Multiple access
Multiple access
-
 Cleavage
Cleavage
-
 Large Magellanic cloud
Large Magellanic cloud
-
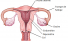 Uterus
Uterus
-
 Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsin
-
 Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
-
 Therapy
Therapy
-
 Autotrophism
Autotrophism
-
 Clausius-Clapeyron relation
Clausius-Clapeyron relation
-
 Ridge
Ridge
-
 Plaster
Plaster
-
 Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
-
 Oxidation zone
Oxidation zone
-
 Reflected light
Reflected light
-
 Mars Express
Mars Express
Mumps
Mumps (or mumps parotitis) is a viral illness often occurring in childhood, caused by the mumps virus.
The mumps agent
Mumps is an illness caused by the mumps virus that belongs to the Paramyxoviridaefamily. The virus enters the body through the upper respiratory tract. The virus usually only has a tropism limited to human beings.
Transmission of mumps
The virus is transmitted between human beings without contact being necessary. Viral particles can be excreted by the patient's saliva, contaminate the surrounding air and infect a new target.
The targets are generally children, although adults can also be infected. The disease is more severe in adults.
Symptoms of mumps
The respiratory tract infection is initially asymptomatic. The virus then spreads in the blood and colonises the whole body. The initial symptoms only develop in the salivary glands after a long incubation period (three weeks) this produces uni or bilateral parotitis (an infection of the largest salivary gland, the parotid gland). In addition to the salivary glands the virus can develop in all glandular organs including the ovaries, testes (which may cause sterility), pancreas, kidney or even central nervous system causing meningitis or encephalitis.
Treatment of mumps
The treatment is mainly symptomatic: it does not directly target the virus. There is, however, a preventative vaccine which is often given in combination with vaccines against rubella and measles.
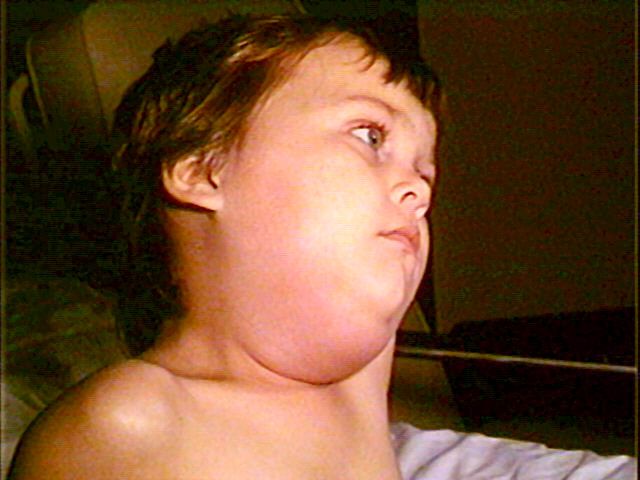 Mumps is a viral disease which affects the salivary glands. © DR
Mumps is a viral disease which affects the salivary glands. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



