-
 Euryhaline
Euryhaline
-
 Semaphore
Semaphore
-
 Disseminated
Disseminated
-
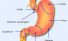 Cardia
Cardia
-
 LPG
LPG
-
 Triple DES
Triple DES
-
 European larch
European larch
-
 Concentration
Concentration
-
 Alternating
Alternating
-
 Massive Compact Halo Objects
Massive Compact Halo Objects
-
 Quinolone
Quinolone
-
 SAFER
SAFER
-
 Vasectomy
Vasectomy
-
 Wigner effect
Wigner effect
-
 BSE
BSE
-
 Spitzer
Spitzer
-
 Lebanon cedar
Lebanon cedar
-
 Sexual selection
Sexual selection
-
 Compressed air engine
Compressed air engine
-
 Quantum number
Quantum number
-
 Heat stability
Heat stability
-
 Mycorrhizas
Mycorrhizas
-
 Ramsar Convention
Ramsar Convention
-
 PSP
PSP
-
 Cremaster
Cremaster
-
 Clinopyroxene
Clinopyroxene
-
 Germinal layer
Germinal layer
-
 Eczema
Eczema
-
 Wave mechanics
Wave mechanics
-
 3GPP
3GPP
Monocyte
Structure of monocytes
Monocytes are large blood cells (from 20 to 40 micrometres in diameter) which are mobile and produced by the bone marrow from haemopoietic stem cells, specifically from monoblasts.
Function of monocytes
These are young leukocytes, which are involved in phagocytosis and haemostasis (coagulation). When monocytes leave the circulating blood, they then evolve into different types of phagocytes:
- macrophages in connective tissue;
- microglial cells in the central nervous system;
- osteoclastes in bone.
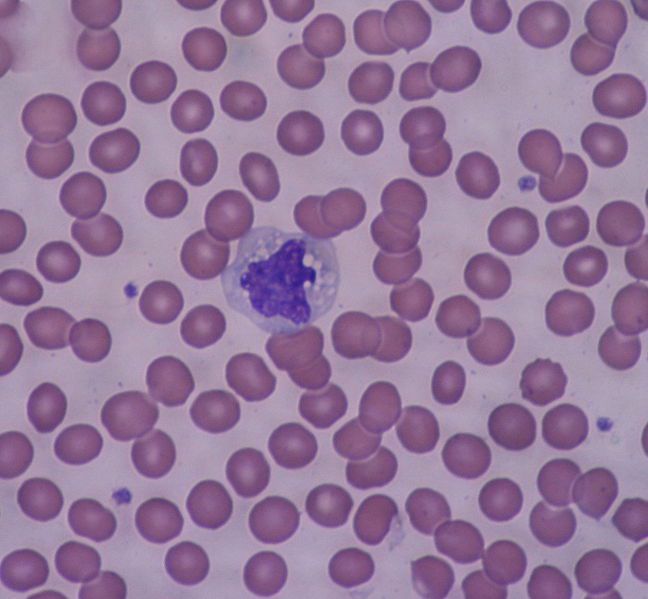 A monocyte surrounded by red blood cells. © Bobjgalindo, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
A monocyte surrounded by red blood cells. © Bobjgalindo, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



