-
 Exergonic
Exergonic
-
 ICT
ICT
-
 Aristolochia
Aristolochia
-
 2.5 G
2.5 G
-
 Scarring
Scarring
-
 Agglutinin
Agglutinin
-
 Protogynous
Protogynous
-
 Sodolithic
Sodolithic
-
 Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen cycle
-
 Codon
Codon
-
 Cosmos 1
Cosmos 1
-
 Gost
Gost
-
 Weatherboarding
Weatherboarding
-
 Contraceptive patch
Contraceptive patch
-
 Absolute zero
Absolute zero
-
 Chromatin
Chromatin
-
 Shareware
Shareware
-
 PLC
PLC
-
 Boot
Boot
-
 Browsing
Browsing
-
 xDSL
xDSL
-
 Ophiolite
Ophiolite
-
 Supination
Supination
-
 Riveting
Riveting
-
 Mycorrhizas
Mycorrhizas
-
 UML
UML
-
 Pillow lavas
Pillow lavas
-
 Thermal energy
Thermal energy
-
 Input
Input
-
 Proton-proton chain
Proton-proton chain
Mammography
Mammography is performed using an instrument specifically dedicated to this purpose: the mammograph. It uses X rays to produce high resolution images of the breast Differences in breast tissue absorption of X rays allow an image to be produced which shows the architecture of the breast. Instruments now use digital techniques. The examination is either performed in a radiology centre or in a hospital radiology department.
Mammography - the process
Mammography can be performed as a screening or diagnostic test for breast cancer. In the first of these instances the investigation is used to detect a cancer which is still too small to be detected by self-examination or by a doctor. In the second situation, the aim is to determine the size and position of the lesion accurately. The examination allows images of the tissue and surrounding ganglia to be produced.
The mammographyprocedure
The mammogram is performed with the person standing. The breast is positioned between a cassette holder and a compression device. In the great majority of cases, two films are taken of each breast: one straight on (postero-anterior) and one oblique, making a total of four films.
Possible risks of mammography
Mammography carries no risk. The doses of radiation used are low. In order to obtain high quality images the breast needs to be compressed during the investigation which is occasionally uncomfortable. It is recommended that a mammogram be performed during the first part of the menstrual cycle or during a period without hormone replacement therapy.
Sources:
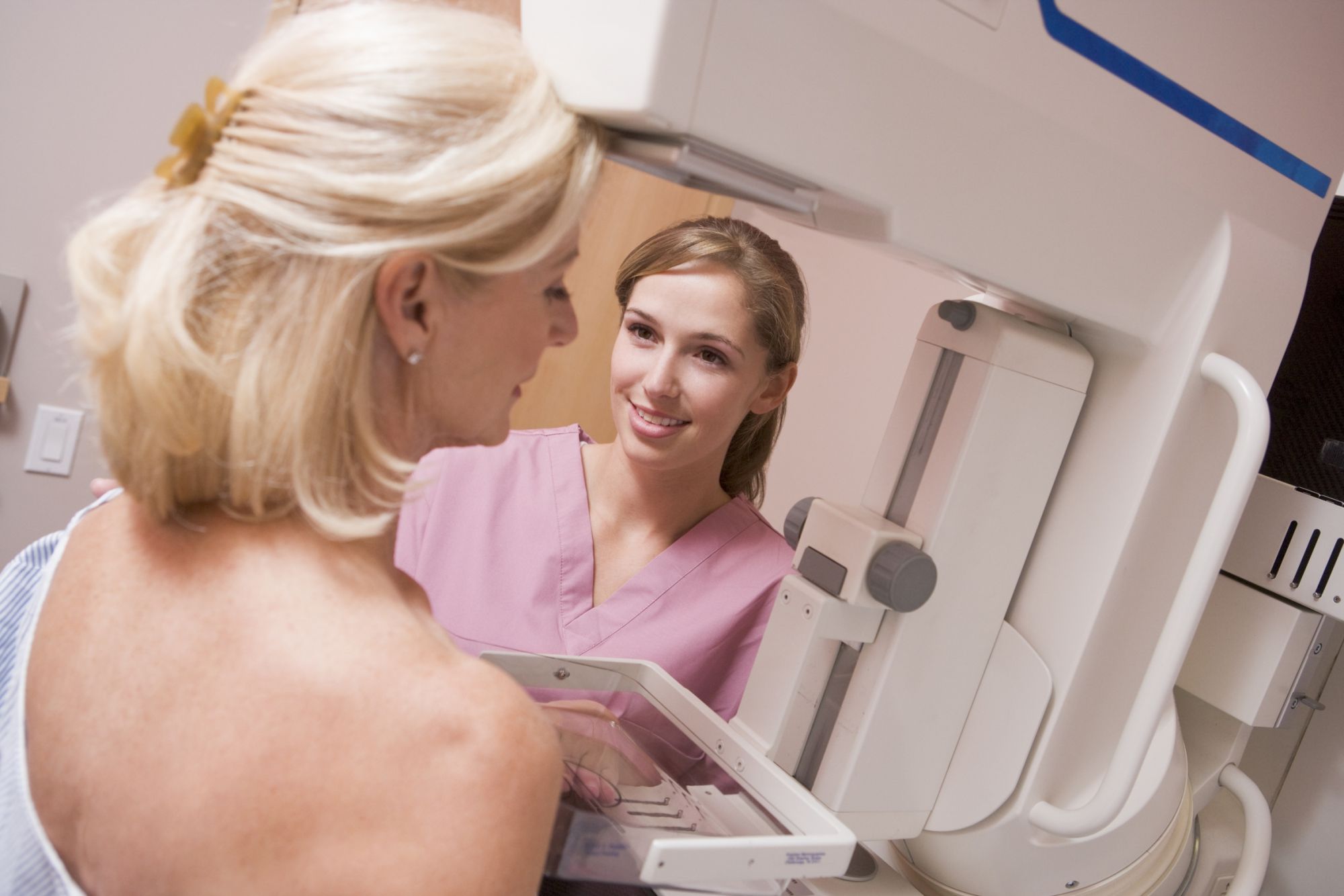 The breast must be compressed to obtain high quality mammography images. © Monkey Business/Fotolia
The breast must be compressed to obtain high quality mammography images. © Monkey Business/Fotolia
Latest
Fill out my online form.



