-
 Calcium
Calcium
-
 Phobos-Grunt
Phobos-Grunt
-
 Barnacle
Barnacle
-
 Wave velocity
Wave velocity
-
 Articular cartilage
Articular cartilage
-
 Exon
Exon
-
 Tuff
Tuff
-
 Trojan horse
Trojan horse
-
 Factorial
Factorial
-
 Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy
-
 Calipso
Calipso
-
 Island arc
Island arc
-
 Anaesthetic
Anaesthetic
-
 Extended area
Extended area
-
 Sub-critical reactor
Sub-critical reactor
-
 Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock
-
 XMP
XMP
-
 Arboreal
Arboreal
-
 Meteorite swarm
Meteorite swarm
-
 Adjuvant
Adjuvant
-
 Genetic Engineering
Genetic Engineering
-
 FFMPEG
FFMPEG
-
 WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG
-
 Pedogenesis
Pedogenesis
-
 Absorption
Absorption
-
 LED
LED
-
 Alkaloid
Alkaloid
-
 Scute
Scute
-
 Stratification
Stratification
-
 Reduced substance
Reduced substance
Macrophage
A macrophage is an immune system cell .
Structure of macrophages
A macrophage is a cell originating from the blood and produced from the transformation of a monocyte.
It is found in tissues which may suffer infections or accumulation of waste which needs to be removed (liver, lungs, lymph nodes, spleen, etc.)
Function of macrophages
Macrophages have three main functions :
- firstly, phagocytosis (ingestion of bacteria, yeasts, cell debris..). The intracellular vesicle formed is called the phagosome, which is carried to the lysosome to be fully degraded;
- secondly, secretory activity (cytokines..) ;
- and thirdly, cell cooperation (this is the antigen presenting cell which communicates with lymphocytes).
They are therefore cells involved in innate immunity as they phagocytose non-specific materials. They are attracted to the site of inflammation by chemotaxis.
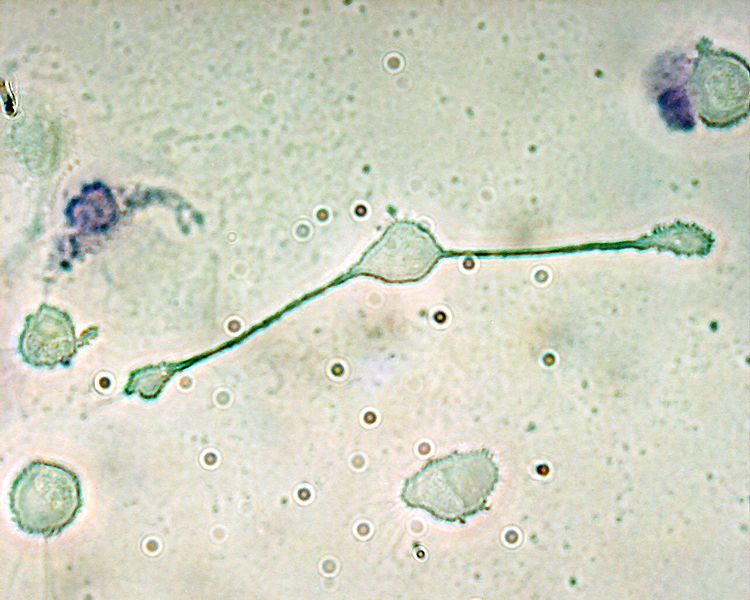 Macrophages can phagocytose foreign bodies. © Obli, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 2.0
Macrophages can phagocytose foreign bodies. © Obli, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



