-
 Hot spring
Hot spring
-
 Mumps virus
Mumps virus
-
 Ophiolite
Ophiolite
-
 Septicaemia
Septicaemia
-
 NGC
NGC
-
 Tack
Tack
-
 Efflorescence
Efflorescence
-
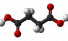 Succinate
Succinate
-
 Graphite
Graphite
-
 Spathe
Spathe
-
 Citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
-
 Cervix
Cervix
-
 Degassing
Degassing
-
 mRNA
mRNA
-
 Hypersaline water
Hypersaline water
-
 PLED
PLED
-
 Encephalitis
Encephalitis
-
 Leukocyte
Leukocyte
-
 Pink siris
Pink siris
-
 Annual parallax
Annual parallax
-
 Cleavage
Cleavage
-
 Wettability
Wettability
-
 Wood energy
Wood energy
-
 Metapopulation
Metapopulation
-
 Bulimia
Bulimia
-
 Scramjet
Scramjet
-
 Antiseptic
Antiseptic
-
 Refractory
Refractory
-
 SQLite
SQLite
-
 Span-wise ice accretion
Span-wise ice accretion
Lamellar bone
Fibrillar bone can be distinguished from Lamellar bone because of the spatial organisation of the extracellular matrix of bone (EMB). Whereas the collagen bundles in fibrillar bone are all arranged in all directions, the structure of the lamellar bone is regular.
Fibrillar bone (or primary or immature, during development or recovery from fracture is therefore formed wherever bone tissue has to be produced very quickly whereas lamellar (or mature) bone is secondary and requires more time to form. Lamellar bone is formed from spongiform or canalicular bone (Spongiosa) and compact bone (Kompakta), which are both lamellar structures. They differ only in how their fibres are arranged. Spongiform bone is formed from flat fibres parallel to the surface whereas compact bone is formed from concentric fibres arranged around a blood vessel. The lamellar structure can be seen under a polarising microscope.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



