-
 LH2
LH2
-
 Exophthalmus
Exophthalmus
-
 Splicing
Splicing
-
 Class I anti-arrhythmic
Class I anti-arrhythmic
-
 Tropopause
Tropopause
-
 Spectrum
Spectrum
-
 Principle of action and reaction
Principle of action and reaction
-
 Semi-permeable membrane
Semi-permeable membrane
-
 Red deer
Red deer
-
 Character
Character
-
 Quaoar
Quaoar
-
 IDS
IDS
-
 Disseminated
Disseminated
-
 Home automation
Home automation
-
 Silurian
Silurian
-
 AVI
AVI
-
 Latitude
Latitude
-
 Plasmon
Plasmon
-
 Chalazion
Chalazion
-
 Gamma ray
Gamma ray
-
 Anther
Anther
-
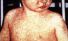 Measles
Measles
-
 Meristem
Meristem
-
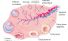 Ovulation
Ovulation
-
 Scots pine
Scots pine
-
 Spectroheliograph
Spectroheliograph
-
 Drizzle
Drizzle
-
 Patina
Patina
-
 Peristalsis
Peristalsis
-
 CMR
CMR
Herpes
Herpes is a common infection caused by a virus. Herpes is usually mild but can be serious in a patient treated for cancer.
There are two types of herpes simplex virus: hsv1 and hsv2. Their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is similar in shape and organisation. 50% of their DNA is identical although their pathogenic potential, epidemiology, and usual clinical features on the skin or mucous membranes are different.
The viruses are fragile and can only be transmitted by direct skin or mucosal contact: kissing, hands contaminated by saliva, skin breaks, sexual intercourse, or childbirth. After initial contact (primary infection), which may or may not be apparent, the virus multiplies at the inoculation site and then spreads through the blood or along the nerves.
The usual lesions of herpes are vesicles on the skin or mucosal membranes. hsv1 infects the lips (cold sores) or the mouth and hsv2 affects the genital mucous membranes.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



