-
 Coelom
Coelom
-
 Data protection act
Data protection act
-
 Glass mat
Glass mat
-
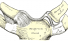 Manubrium
Manubrium
-
 Infrared
Infrared
-
 Endoderm
Endoderm
-
 Orexin neurone
Orexin neurone
-
 Cryptomeria
Cryptomeria
-
 Cerebral ventricle
Cerebral ventricle
-
 Integrity
Integrity
-
 HIV
HIV
-
 GAK
GAK
-
 Prosthesis
Prosthesis
-
 Class
Class
-
 Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis
-
 IFREMER
IFREMER
-
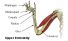 Humerus
Humerus
-
 Corpuscle
Corpuscle
-
 Horizontal coordinates of a direction
Horizontal coordinates of a direction
-
 Diplegia
Diplegia
-
 Uterine relaxant
Uterine relaxant
-
 Electronic configuration
Electronic configuration
-
 Basiphilous
Basiphilous
-
 Diapir
Diapir
-
 Turbopump
Turbopump
-
 Natural CO2 sequestering
Natural CO2 sequestering
-
 Goldschmidt classification
Goldschmidt classification
-
 Lacunar circulation
Lacunar circulation
-
 Waste-to-energy
Waste-to-energy
-
 Pre-neoplastic lesion
Pre-neoplastic lesion
Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (Glu, E or glutamate) is one of the 22 amino acids of which proteins are made.
Structure of glutamic acid
Like all amino acids, glutamic acid has two functional groups: a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2). It has the following side chain: -CH2-CH2-COOH.
It is therefore a dicarboxylic polar acid amino acid.
Function of glutamic acid
As glutamic acid can be synthesised by the body from alpha-ketoglutarate, it is not an essential amino acid.
Glutamic acid is the most widely found neurotransmitter in the body.
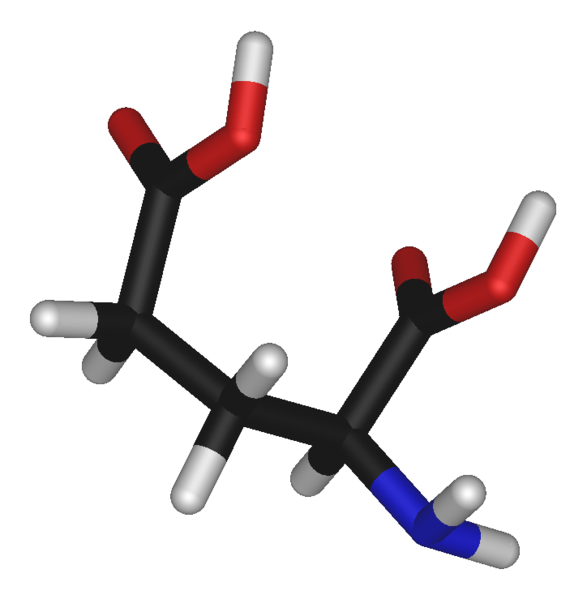 Glutamic acid is an amino acid and also an important neuromediator (carbon in black, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and hydrogen in white). © Photohound, public domain
Glutamic acid is an amino acid and also an important neuromediator (carbon in black, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and hydrogen in white). © Photohound, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



