-
 Metamict
Metamict
-
 Genetics
Genetics
-
 Pomegranate
Pomegranate
-
 Fluorescence
Fluorescence
-
 Axillary
Axillary
-
 Perihelion
Perihelion
-
 Draconitic period
Draconitic period
-
 Telematics
Telematics
-
 Tsunami
Tsunami
-
 Group of galaxies
Group of galaxies
-
 Gibbous moon
Gibbous moon
-
 Nuptial plumage
Nuptial plumage
-
 FDMA
FDMA
-
 Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis
-
 Alar bar
Alar bar
-
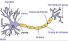 Dendrite
Dendrite
-
 Cathode
Cathode
-
 Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
-
 Semi-conductor
Semi-conductor
-
 Pancreatectomy
Pancreatectomy
-
 Windows XP
Windows XP
-
 Dyspraxia
Dyspraxia
-
 Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis
-
 Frostbite
Frostbite
-
 Haemoccult
Haemoccult
-
 Photochemical pollution
Photochemical pollution
-
 Measles virus
Measles virus
-
 Volcano
Volcano
-
 Anatidae
Anatidae
-
 Analemma
Analemma
Glucagon
Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, the role of which is to stimulate the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
Structure of glucagon
Glucagon has a relatively simple structure as it is a relatively small peptide containing only 29 amino acids. It is produced in the pancreas by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Function of glucagon
Glucagon has a hormonal function that counters insulin, causing an increase in blood glucose (hyperglycaemic function). It hydrolyses glycogen in the liver to do this causing release of glucose molecules into the blood. This effect is called glycogenolysis.
Regulation of the action of insulin and glucagon maintains a correct blood glucose concentration appropriate for the body's efforts.
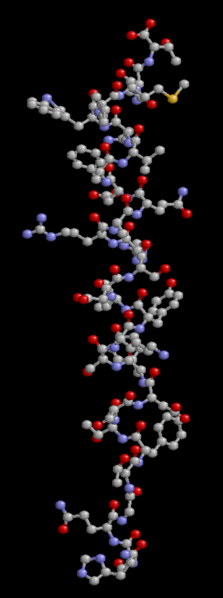
Glucagon is a relatively short peptide hormone. © brian0918, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



