-
 Livery
Livery
-
 Hygrometry
Hygrometry
-
 Metabolism
Metabolism
-
 Pallasite
Pallasite
-
 Fluorine
Fluorine
-
 Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
-
 Myeloma
Myeloma
-
 Granulocytopenia
Granulocytopenia
-
 Télétel
Télétel
-
 Eisenmenger complex
Eisenmenger complex
-
 Lysosome
Lysosome
-
 Landsat
Landsat
-
 Microfiltration
Microfiltration
-
 Eris
Eris
-
 Glioma
Glioma
-
 Isomerism
Isomerism
-
 Douglas fir
Douglas fir
-
 Raman effect
Raman effect
-
 Subadult
Subadult
-
 XMM-Newton satellite
XMM-Newton satellite
-
 Sea ice - First year thick
Sea ice - First year thick
-
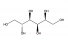 Sorbitol
Sorbitol
-
 Diester
Diester
-
 Corti cell
Corti cell
-
 Thylakoid
Thylakoid
-
 Allosome
Allosome
-
 Glycogen
Glycogen
-
 Interface
Interface
-
 Peristalsis
Peristalsis
-
 Fetal
Fetal
Ergotamine
Ergotamine is derived from rye ergot and can only be used for the curative treatment of a migraine attack and not for prevention. Since the arrival of the triptans, however, these medicines are not widely used because of their side effects of nausea and vomiting.
How does ergotamine work?
Ergotamine, which is prepared as ergotamine tartrate by adding tartaric acid as an excipient, has an alpha agonist and therefore vasoconstricting effect. As a result it reduces the arterial dilatation, which is caused by the migraine attack, and the related pain. It also acts on serotonin receptors.
Do they have contraindications or precautions?
The main side effects reported with these treatments are nausea, palpitations, drowsiness, cramps and tingling in the lower limbs. More rarely, they can cause habituation and may lead to status migrainosus. Another rare but recognised effect is ergotism. This produces severe vasoconstriction which may lead to ischaemia of the extremities and gangrene. These medicines are contraindicated in hypertension, arterial disease, coronary artery disease and severe hepatic impairment and in pregnancy. In addition, ergotamine is incompatible with antibiotics belonging to the macrolide family and with triptans.
 Ergotamine to treat migraine attacks. © Phovoir
Ergotamine to treat migraine attacks. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



