-
 Quartzite
Quartzite
-
 EADS
EADS
-
 Sex chromosome
Sex chromosome
-
 Triploblastic
Triploblastic
-
 Calciphile
Calciphile
-
 Diamond
Diamond
-
 Dry process
Dry process
-
 Local group
Local group
-
 Larynx
Larynx
-
 Stem cell
Stem cell
-
 ECC
ECC
-
 Hem
Hem
-
 Axon
Axon
-
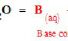 Acid
Acid
-
 Pulsar
Pulsar
-
 Mercalli scale
Mercalli scale
-
 Van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
-
 Melliferous
Melliferous
-
 Frost
Frost
-
 Black-veined white
Black-veined white
-
 Liquid laser
Liquid laser
-
 Key splitting
Key splitting
-
 Glycolipid
Glycolipid
-
 Antacids
Antacids
-
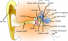 Cochlea
Cochlea
-
 Endemic
Endemic
-
 Pelleting
Pelleting
-
 Milky Way
Milky Way
-
 Emphyteusis
Emphyteusis
-
 Translucent
Translucent
Epstein-Barr virus
The Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, causes infectious mononucleosis and some cancers.
Features of the Epstein-Barr virus
EBV belongs to the Herpesviridae family, and the Lymphocryptovirus genus. It has a 172,000 base pair linear double-stranded DNA genome. It codes for many viral proteins (around 100), expression of which is finely regulated.
The DNA is contained within a viral protein capsid which is covered by a coating and a lipid membrane which is obtained from the cell.
Epstein-Barr virus and mononucleosis
The mononucleosis virus is transmitted in saliva, hence it is also called the kissing disease. The virus has B lymphocyte tropism as a result of viral surface proteins binding to cell receptors. Once it has gone into the cell it enters the lytic phases, multiplying, or the latent phase, and is replicated at the same time as the cell DNA.
The virus is also implicated in malignant diseases, such as Burkitt's lymphoma.
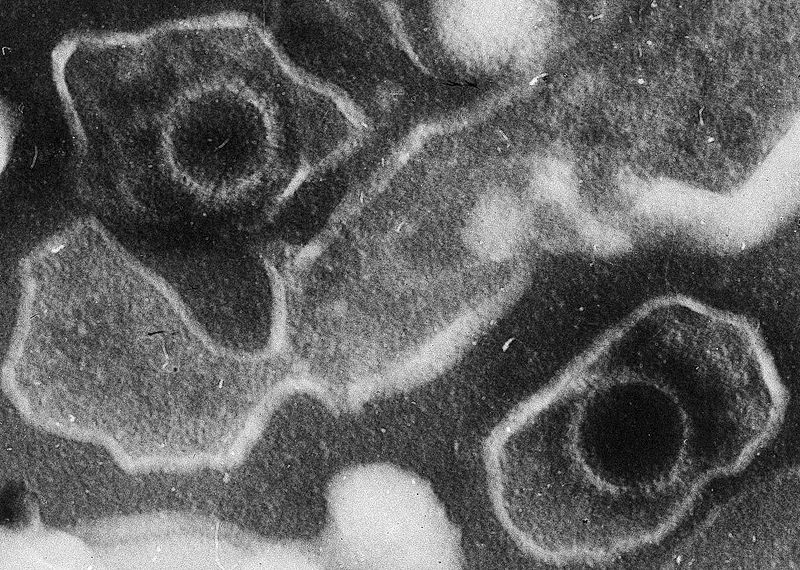 Epstein-Barr virus causes infectious mononucleosis. © Liza Gross, Wikimedia, CC by 2.5
Epstein-Barr virus causes infectious mononucleosis. © Liza Gross, Wikimedia, CC by 2.5
Latest
Fill out my online form.



