-
 D meson
D meson
-
 HELIOS
HELIOS
-
 Melanocyte
Melanocyte
-
 Audiotex
Audiotex
-
 Denial of service
Denial of service
-
 Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri
-
 Byssus
Byssus
-
 Spectral classification
Spectral classification
-
 Relative permeability
Relative permeability
-
 Hypocentre
Hypocentre
-
 Mean free path
Mean free path
-
 Brightening
Brightening
-
 EER
EER
-
 VLBI
VLBI
-
 Artemisin
Artemisin
-
 RSS
RSS
-
 Groin
Groin
-
 Tunnel effect
Tunnel effect
-
 Planetocentric coordinates
Planetocentric coordinates
-
 Relenza
Relenza
-
 Miocene
Miocene
-
 Holothurian
Holothurian
-
 Sea ice - Grey
Sea ice - Grey
-
 Ion channels
Ion channels
-
 Germicide
Germicide
-
 Proton
Proton
-
 Epiphysis
Epiphysis
-
 Lamellar bone
Lamellar bone
-
 Amyotrophy
Amyotrophy
-
 Moisture regime
Moisture regime
Ebola Virus
Ebola virus (or Ebolavirus) belongs to the Filoviridae family and is responsible for a serious haemorrhagic fever.
Characteristics of the Ebolavirus
There are four sub-types of the Ebola virus belonging to the Filoviridaefamily:
- Zaire;
- Sudan;
- Ivory Coast;
- and Reston.
Three of the viral sub-types found in the Democratic Republic of Congo (formerly Zaire), the Sudan, and the Ivory Coast are pathogenic to human beings.
TheEbolavirus is a filamentous virus almost 1 micrometre long and 80 nanometres in diameter. It has a large negative polarity RNA genome (which does not code directly) of 18 to 19,000 nucleotide which codes for 7 proteins. The genome bound to proteins is encapsulated by matrix proteins, the layer in which the glycoproteins are anchored.
Ebolavirus and haemorrhagic fever
The Ebola virus is transmitted by direct contact with blood, secretions, organs or biological fluids of infected people. The first cells affected are believed to be mononuclear cells in the phagocytic system. The virus tropism then extends to the epithelial cells, fibroblasts, or hepatocytes through the action of the glycoproteins located on the surface of the viral particles.
The haemorrhagic fever caused by the Ebola virus is fatal in 50% to 90% of patients with clinical features.
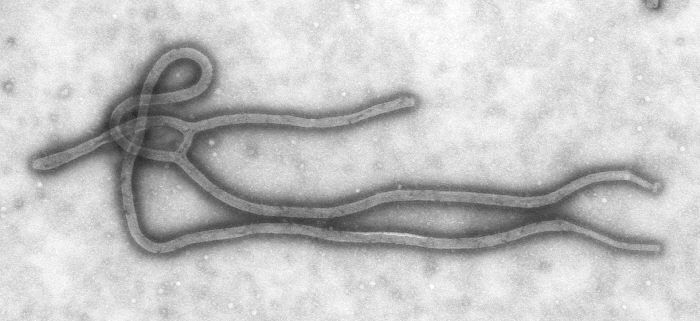 The Ebola virus has a filamentous viral particle. © DR
The Ebola virus has a filamentous viral particle. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



