-
 Sequella
Sequella
-
 Centriole
Centriole
-
 Heterotrophic
Heterotrophic
-
 Concave
Concave
-
 DART
DART
-
 Inhalation
Inhalation
-
 Nanoparticle
Nanoparticle
-
 Trypanosome
Trypanosome
-
 Low molecular weight heparin
Low molecular weight heparin
-
 Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
-
 Lactase
Lactase
-
 Sarking
Sarking
-
 Exon
Exon
-
 Avalanche
Avalanche
-
 Proper motion of a star
Proper motion of a star
-
 ECS
ECS
-
 Hour circle of a direction
Hour circle of a direction
-
 Cambrian
Cambrian
-
 Eupnoea
Eupnoea
-
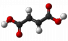 Fumarate
Fumarate
-
 Triangle galaxy
Triangle galaxy
-
 Visual pollution
Visual pollution
-
 Focal length
Focal length
-
 Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle
-
 Jatropha
Jatropha
-
 Zoonosis
Zoonosis
-
 UEPS
UEPS
-
 Photovoltaic solar energy
Photovoltaic solar energy
-
 Redshift
Redshift
-
 IP address
IP address
Beta blocker
These medicines have been used in cardiology since the middle of the 1960s. These medicines reduce blood pressure and are indicated to treat heart failure, angina pectoris, hypertension, myocardial infarction, and episodes of tachycardia etc. Beta blockers and diuretics are still the treatments of choice forInhypertension.
How do beta blockers work?
Their main method of action is to reduce the activity of the nervous system. After an initial latent period, they reduce hypertension through complex mechanisms of reducing heart rate and inhibiting secretion of renin, an enzyme required for the formation of angiotensin II. The anti-hypertensive effect of these medicines is obtained at low doses.
Do they have contraindications or do they need precautions for use?
These medicines can cause weakness, cold extremities (Raynaud's disease), bradycardia (abnormal slowing of the heart rate), gastro-intestinal problems (diarrhoea, epigastric pain, nausea or vomiting), and reduced physical performance during exercise.
Sources :
- Merck Manual – 4th edition
- Comité français de lutte contre l'hypertension artérielle (French hypertension committee), website accessed on 17 June 2011
- Pharmacorama, website accessed on 17 June 2011
 Beta blockers reduce heart rate. © DR
Beta blockers reduce heart rate. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



