-
 Colour rendering index
Colour rendering index
-
 European black pine
European black pine
-
 DVI
DVI
-
 Ailanthus
Ailanthus
-
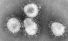 SARS-CoV
SARS-CoV
-
 Mica-schist
Mica-schist
-
 Rhizome
Rhizome
-
 Bacterium
Bacterium
-
 Cosmic ray
Cosmic ray
-
 Hemiptera
Hemiptera
-
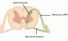 Interneurone
Interneurone
-
 Etna
Etna
-
 VBR
VBR
-
 Haemodynamics
Haemodynamics
-
 Pegasus
Pegasus
-
 Plutonium
Plutonium
-
 Magnetopause
Magnetopause
-
 Sun
Sun
-
 Genetic code
Genetic code
-
 Phase space
Phase space
-
 Okra
Okra
-
 Schweizerhalle disaster
Schweizerhalle disaster
-
 Cochlear implant
Cochlear implant
-
 TDG risk
TDG risk
-
 Dark matter
Dark matter
-
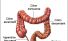 Colon
Colon
-
 Hale-Bopp comet
Hale-Bopp comet
-
 Lateral chromatic aberration
Lateral chromatic aberration
-
 Nesosilicates
Nesosilicates
-
 Cone
Cone
Beta-agonist bronchodilator
The beta-agonist group of bronchodilators, also called the beta-adrenergics, are short-acting medicines . They are used to treat and prevent bronchoconstriction, an abnormal contraction of bronchial wall muscles. They are usually administered by inhalation.
How do the beta-agonist bronchodilators work?
These bronchodilators relax bronchial muscles, promoting the passage of air into the lungs. They have a rapid onset of action and produce their effect in a few minutes. They are therefore indicated in acute attacks.
Do they have contraindications or precautions?
The beta-antagonist bronchodilators can cause heart palpitations, irritability, difficulty sleeping, muscle cramps and tremor. Usually the side effects diminish after using the medicine for a certain length of time.
Source: Merck Manual, 4th edition
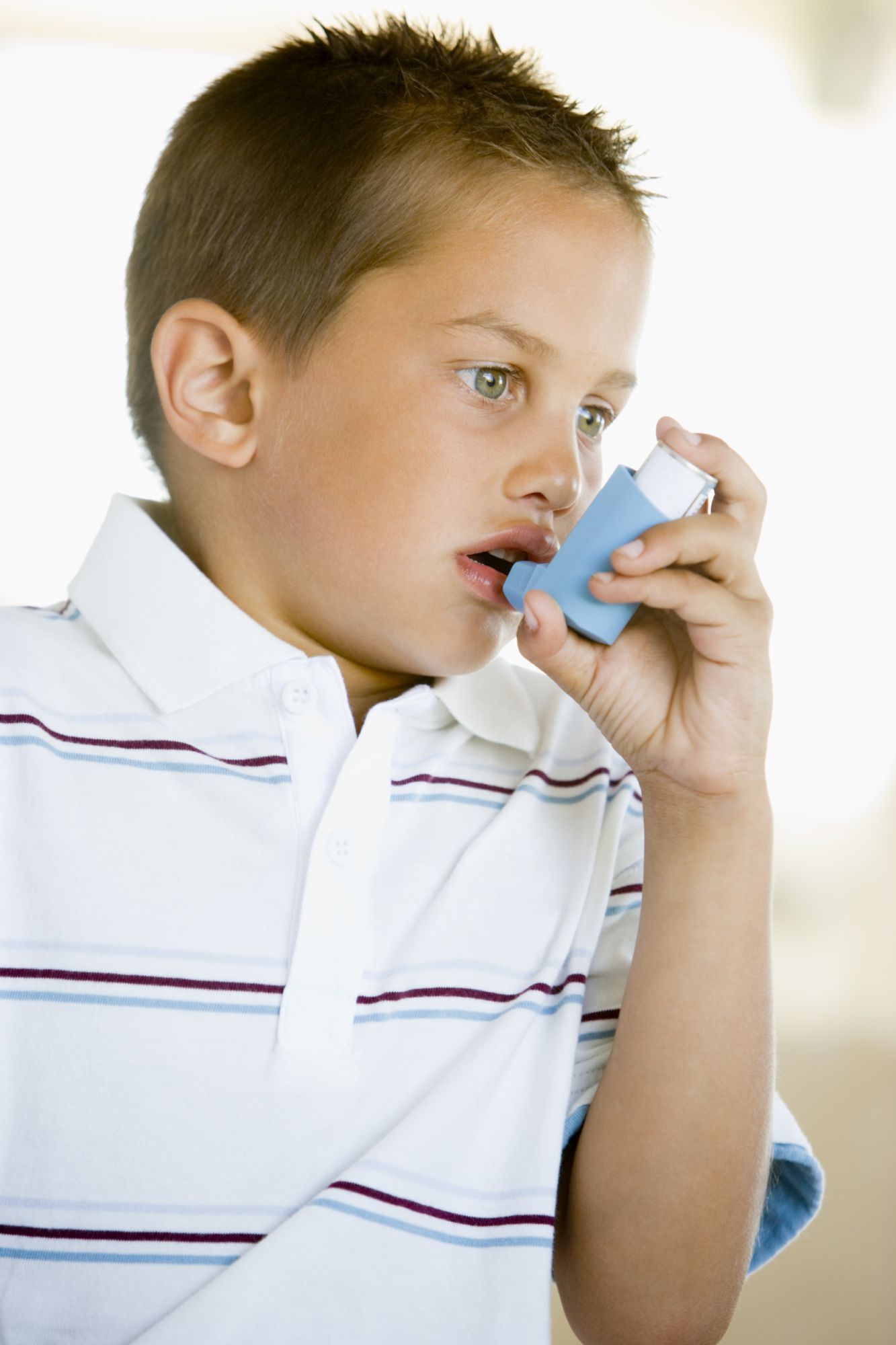 The beta-agonist bronchodilators treat abnormal contraction of the bronchial wall muscles. © Phovoir
The beta-agonist bronchodilators treat abnormal contraction of the bronchial wall muscles. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



