-
 Anti-EGFR
Anti-EGFR
-
 Chloroplast
Chloroplast
-
 Domain name
Domain name
-
 Asbestos
Asbestos
-
 Cheiropompholyx
Cheiropompholyx
-
 H1 histamine antagonist
H1 histamine antagonist
-
 Antigorite
Antigorite
-
 IRD
IRD
-
 UEPS
UEPS
-
 Endorphins
Endorphins
-
 Mars
Mars
-
 Replicase
Replicase
-
 Robot
Robot
-
 Plain text
Plain text
-
 Biofilter
Biofilter
-
 Naevus
Naevus
-
 NRO
NRO
-
 Huntington's Disease
Huntington's Disease
-
 GDP
GDP
-
 ISO 14.001
ISO 14.001
-
 Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine
-
 Computer network
Computer network
-
 Acini
Acini
-
 Zygote
Zygote
-
 Endocrine
Endocrine
-
 Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris
-
 Beaufort scale
Beaufort scale
-
 Host
Host
-
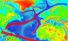 Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream
-
 Pheromone
Pheromone
Atrial flutter
The name flutter comes from its English origin, which means beating of wings. In medicine it means a tachycardia involving very fast but regular contractions of the atria (or ventricles). It is diagnosed from an electrocardiogram (ECG).
When it is accompanied by the descriptive term atrial, the flutter obviously means contractions of the cardiac atria. These contract at a rate of 250 to 350 beats per minute, which is extremely fast. The major symptoms of atrial flutter are palpitations or even persistent tiredness.
What are the risks of atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is less common than atrial fibrillation. This other heart disorder involves irregular contractions of the atria producing a disorganised cardiac rhythm. In both situations the main risk is of a thrombus, i.e. a blood clot forming. This may migrate into the systemic circulation and cause an infarction or cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
As in atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is treated by controlling the heart rate. And preventing thromboembolism.
Source:
- Grenoble Faculty of Medicine, website accessed on 18 October 2011
- Merck Manual, Fourth edition.
 Atrial flutter describes a heart which is beating fast and regularly. © Phovoir
Atrial flutter describes a heart which is beating fast and regularly. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



