-
 Walking bus
Walking bus
-
 Turner's Syndrome
Turner's Syndrome
-
 Respiratory system
Respiratory system
-
 Dose
Dose
-
 Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine
-
 Phobos
Phobos
-
 NEAR-Shoemaker
NEAR-Shoemaker
-
 Loose pack ice
Loose pack ice
-
 ADP
ADP
-
 A5
A5
-
 Functional isomerism
Functional isomerism
-
 Clean coal
Clean coal
-
 Autoclaved aerated concrete
Autoclaved aerated concrete
-
 Kohoutek comet
Kohoutek comet
-
 Anatidae
Anatidae
-
 Absolute zero
Absolute zero
-
 Skarn
Skarn
-
 Haemolytic anaemia
Haemolytic anaemia
-
 Tidal bore
Tidal bore
-
 Tropical forest
Tropical forest
-
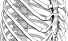 Sternum
Sternum
-
 Endemic stick insect (apterograeffa reunionensis)
Endemic stick insect (apterograeffa reunionensis)
-
 Scute
Scute
-
 Diester
Diester
-
 Ferrofluid
Ferrofluid
-
 Coalescence
Coalescence
-
 Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia
-
 STED microscopy
STED microscopy
-
 Calcitonin
Calcitonin
-
 Hybrid hard drive
Hybrid hard drive
Antiparkinsonian
The antiparkinsonian agents are medicines used to treat Parkinson's Disease and its consequences. There are now five main categories of these.
The different antiparkinsonian agents
- Levodopa (L-dopa) is the most commonly used antiparkinsonian medicine . This is converted into synthetic dopamine in the patient's body. It does, however, cause many central nervous system complications: motor fluctuations, involuntary movements and drowsiness.
- The dopamine agonists act directly on the dopamine receptors. These synthetic compounds are administered in association with L-dopa and mimic the action of dopamine.
- MAO-B (monoamine oxidase B) inhibitors reduce the degradation of dopamine.
- Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors have the same effect as the MAO-B inhibitors. They therefore increase the effectiveness of dopamine.
- The anticholinergics are being used increasingly less.
Sources:
- Interview with Jean-Philippe Brandel, neurologist at the Léopold Bellan Hospital, Paris, on www.infopatients-lundbeck.fr , 7 July 2011
- MyPDinfo.com, 7 July 2011
 There are five categories of medicines to treat Parkinson's disease. © Phovoir
There are five categories of medicines to treat Parkinson's disease. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



