-
 Calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate
-
 Mimas
Mimas
-
 Allergen
Allergen
-
 Microclimate
Microclimate
-
 Stratification
Stratification
-
 Magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
-
 Aphotic zone
Aphotic zone
-
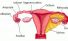 Fallopian tubes
Fallopian tubes
-
 Allosteric site
Allosteric site
-
 RGB
RGB
-
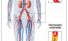 Arteritis
Arteritis
-
 SARS
SARS
-
 Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory
-
 Constellation of Ursa Major
Constellation of Ursa Major
-
 Breast-shield
Breast-shield
-
 Lore
Lore
-
 Morbidity
Morbidity
-
 Full Moon
Full Moon
-
 Coronagraph
Coronagraph
-
 PCI
PCI
-
 Milk teeth
Milk teeth
-
 Ammon's horn
Ammon's horn
-
 Cryptomeria
Cryptomeria
-
 Sun-synchronous
Sun-synchronous
-
 Beta lactam
Beta lactam
-
 James Webb space telescope
James Webb space telescope
-
 Porphyry
Porphyry
-
 Duplex
Duplex
-
 EPO
EPO
-
 Decarbonation
Decarbonation
Anti-fungal
The anti-fungals (or anti-fungal agents) take their name from the Latin fungus which means mushrooms. They are medicinal products which can treat fungal infections, i.e. infections caused by microscopic fungi.
How do the anti-fungals act?
An anti-fungal acts:
- by either directly attacking the wall of the fungus, causing the cell to die (fungicidal activity) ;
- or by blocking cell division, arresting reproduction of the fungus (fungistatic action).
Local anti-fungals need to be distinguished from systemic anti-fungals. Fungal infections are usually found on the skin, hair, or mucosal membrane, etc. In this case an anti-fungal is usually used locally as a cream or powder. In other cases, if the fungal infection is less "accessible" (beneath a nail for example), local treatment may be combined with another treatment either injectable or orally .
Deep fungal infections mostly affect people with a weakened immune system: transplant patients, patients suffering from disorders such as HIV/Aids, or some heroin addicts. They can also occur because of intolerance to certain antibiotics. These disorders are treated with medicinal products which are administered either orally or by injection.
Source : Principles of Internal Medicine, TR Harrison, Ed. Flammarion
 The antifungals combat fungi. © Phovoir
The antifungals combat fungi. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



