-
 Piscivore
Piscivore
-
 Glucagon
Glucagon
-
 Terrestrial meridian of a location
Terrestrial meridian of a location
-
 Celsius
Celsius
-
 E=mc²
E=mc²
-
 Oakley
Oakley
-
 Intrauterine device
Intrauterine device
-
 Glutamine
Glutamine
-
 Nuclear reaction
Nuclear reaction
-
 Post-operative
Post-operative
-
 Opportunity
Opportunity
-
 Heat lightning
Heat lightning
-
 Mullerian mimicry
Mullerian mimicry
-
 Switched virtual circuit
Switched virtual circuit
-
 CAPI
CAPI
-
 Tetanus
Tetanus
-
 Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy
-
 Pseudomorph
Pseudomorph
-
 Subadult
Subadult
-
 Haemagglutinin
Haemagglutinin
-
 Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis
-
 Bayer name
Bayer name
-
 Permanent virtual circuit
Permanent virtual circuit
-
 Mucilage
Mucilage
-
 Carding
Carding
-
 Norway maple
Norway maple
-
 Ergotamine
Ergotamine
-
 Hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
-
 Infection
Infection
-
 Unknown
Unknown
Analgesic anaesthesia
Analgesic anaesthetics (or anaesthetising agents) are a family of medicines used in anaesthesia and intensive care. They are also described as morphine derivatives and are used forgeneral anaesthesiaprocedures. In other words, they put the patient to sleep during surgery.
How do analgesic anaesthetics work?
The analgesic anaesthetics act on central nervous system receptors. They block transmission of the pain signals. They are administered intravenously by an anaesthetist - intensive care physician.
Do they have any contraindications or precautions?
The side effects of these analgesic anaesthetics include nausea, vomiting, and altered consciousness. However, their main risk is that of respiratory depression.
Source: Interview with Dr Véronique Bazin, anaesthetist at the Nantes University Hospital, 16 June 2011
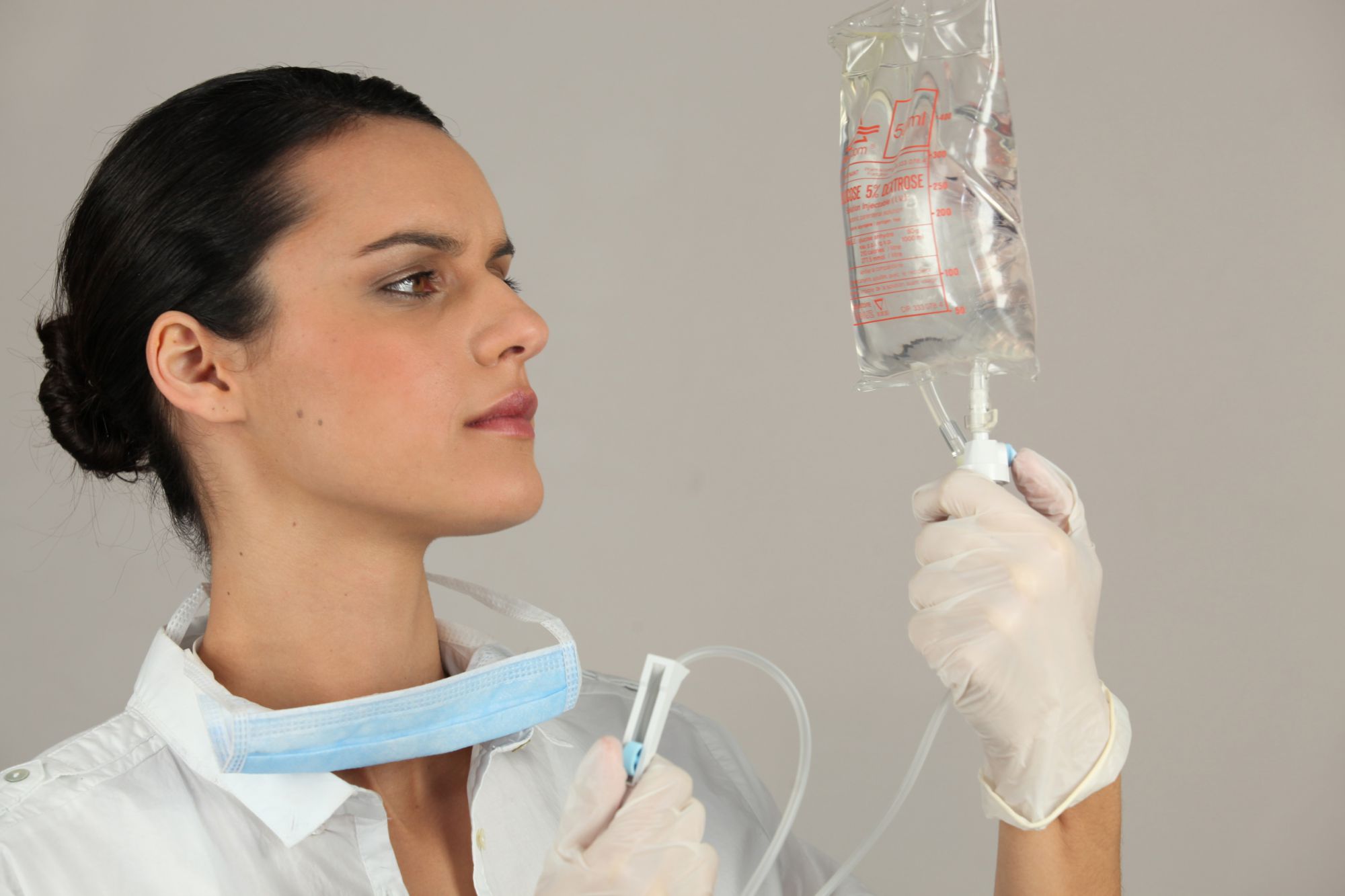 Analgesic anaesthetics are also called morphine derivatives. © Phovoir
Analgesic anaesthetics are also called morphine derivatives. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



