-
 Pectineus
Pectineus
-
 Aurora
Aurora
-
 Plutoid
Plutoid
-
 Conduction block
Conduction block
-
 Spawning ground
Spawning ground
-
 Cytokine
Cytokine
-
 Caffeine
Caffeine
-
 Codon
Codon
-
 Neoteny
Neoteny
-
 Polymetallic
Polymetallic
-
 Pike
Pike
-
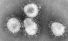 SARS-CoV
SARS-CoV
-
 Pineapple
Pineapple
-
 Montrachet
Montrachet
-
 Constellation of Capricorn
Constellation of Capricorn
-
 Clays (minerals)
Clays (minerals)
-
 Proton-proton chain
Proton-proton chain
-
 Mersenne prime
Mersenne prime
-
 Ophiolite
Ophiolite
-
 Balanced flue boiler
Balanced flue boiler
-
 Proxy
Proxy
-
 Spinal cord
Spinal cord
-
 Brönsted acid
Brönsted acid
-
 PAD
PAD
-
 Reflected light
Reflected light
-
 STD
STD
-
 Pseudo-random number
Pseudo-random number
-
 Boreal forest
Boreal forest
-
 Gost
Gost
-
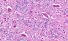 Motor neurone
Motor neurone
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme belonging to the hydrolase family which mainly catalyses the hydrolysis of starch.
Structure of amylase
Amylase is a protein enzyme . It is produced by the salivary glands and the pancreatic glands, and is therefore found in saliva and pancreatic juice. The two enzymes are not identical although they both belong to the class of α-amylases.
The amylases are also found in plants and micro-organisms.
Function of amylase
Amylase is a saccharidase, that is, an enzyme which hydrolyses glucose bonds. In particular, it is involved in degrading starch (famylose and amylopectin) to produce disaccharide sugars (such as maltose).
Salivary amylase is therefore responsible for the sweet taste of foods (due to the development of disaccharides) which are generally not sweet (such as rice that contains starch, which has a very weak sweetening ability).
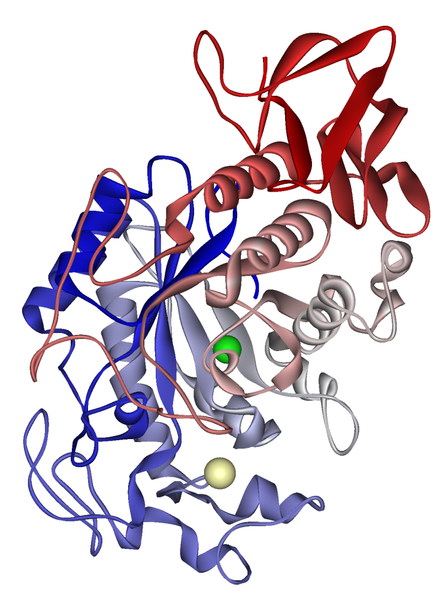 Salivary amylase is a salivary enzyme. © PDB
Salivary amylase is a salivary enzyme. © PDB
Latest
Fill out my online form.



