-
 Pinot noir
Pinot noir
-
 Anisotropy
Anisotropy
-
 Mediastinum
Mediastinum
-
 Dysmetria
Dysmetria
-
 Kebira crater
Kebira crater
-
 Fishery resource
Fishery resource
-
 Perigranitic
Perigranitic
-
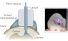 Optogenetics
Optogenetics
-
 Motherboard
Motherboard
-
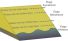 Foreshore
Foreshore
-
 Essential amino acids
Essential amino acids
-
 Canopy
Canopy
-
 Conflict
Conflict
-
 Turnip
Turnip
-
 Extranet
Extranet
-
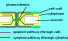 Symplast
Symplast
-
 PGP
PGP
-
 Homeosis
Homeosis
-
 Transplant organ or tissue
Transplant organ or tissue
-
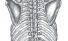 Scapula
Scapula
-
 Oil spill
Oil spill
-
 Cervical cap
Cervical cap
-
 Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy
-
 Disseminated deposit
Disseminated deposit
-
 Q fever
Q fever
-
 Jizz
Jizz
-
 Coal
Coal
-
 Nidifugous
Nidifugous
-
 Homology
Homology
-
 Fibril
Fibril
Heat pump
A heat pump is a non-combustion heating system that extracts heat from the exterior environment to heat the home. In other words, it's the "opposite" of a refrigerator. Heat is usually captured from the air (aerothermal) or the ground (geothermal). Heat may be provided in the form of hot air or hot water. Its energy, economic and ecological value is not always clear, and must be studied case by case.
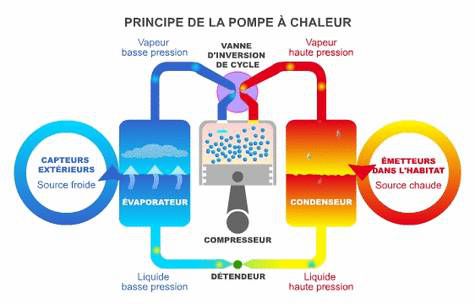 A heat pump operates in the same way as a refrigerator. The fluid circulates on the exterior and takes the temperature of the air or water. It is evaporated after the pressure imposed by the compressor drops (its piston descends). Its temperature lowers, the external source cools. When it rises, the piston warms the fluid that is then sent throughout the home. © AFPAC
A heat pump operates in the same way as a refrigerator. The fluid circulates on the exterior and takes the temperature of the air or water. It is evaporated after the pressure imposed by the compressor drops (its piston descends). Its temperature lowers, the external source cools. When it rises, the piston warms the fluid that is then sent throughout the home. © AFPAC
Latest
Fill out my online form.



