-
 Ice shelf
Ice shelf
-
 Dermis
Dermis
-
 Dormant
Dormant
-
 Peridural
Peridural
-
 Natural CO2 sequestering
Natural CO2 sequestering
-
 Peach
Peach
-
 MAN
MAN
-
 Mirabelle plum
Mirabelle plum
-
 Playlist
Playlist
-
 Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
-
 European crab apple
European crab apple
-
 Speleogenesis
Speleogenesis
-
 Voice synthesis
Voice synthesis
-
 Risk factor
Risk factor
-
 Deep Space 2
Deep Space 2
-
 Minitel
Minitel
-
 Lactitol
Lactitol
-
 Dolby
Dolby
-
 Oncogene
Oncogene
-
 Anisotropic
Anisotropic
-
 Charon
Charon
-
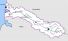 Drainage basin
Drainage basin
-
 Magma
Magma
-
 Zenith distance of a direction
Zenith distance of a direction
-
 Magnaporthe grisea
Magnaporthe grisea
-
 Cosmic ray
Cosmic ray
-
 Webcam
Webcam
-
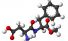 Aspartame
Aspartame
-
 Corsican pine
Corsican pine
-
 Magnetometer
Magnetometer
Embodied energy
The concept of embodied energy appeared in the wake of the HQE (Haute Qualite Environnementale, or High Quality Environmental standard) during the 1970s. It corresponds to the amount of energy used for a product from its conception phase through to its recycling or destruction. Commercialisation or service activities, product use and implementation are some of the criteria considered. The resulting figure allows one to conscientiously choose materials that best respect the environment in each sector. Thus, for insulation material to be considered ecological, it must come from a renewable source, and its collection or extraction must not damage the environment. Likewise, its production must not consume a lot of energy. Finally, it must be entirely recyclable and, as far as possible, produced locally in order to limit transport needs.
Embodied energy, also known as Life Cycle Analysis (or LCA), has become an important selection criterion in construction. In 2002, AFNOR drew up a specific environmental quality standard which includes the energy content of consumer goods : particularly household appliances.
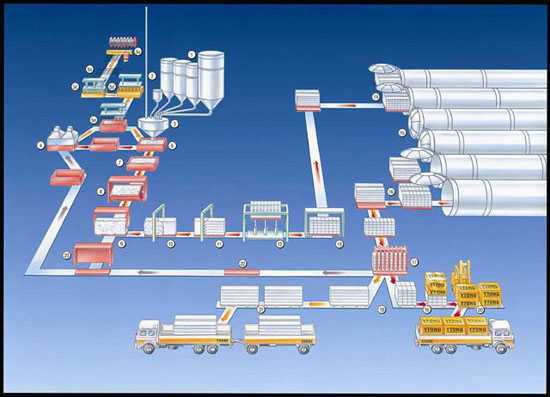 Diagram of a product’s life cycle. The product’s embodied energy is calculated using a global analysis. – Source: Xella-Thermopierre
Diagram of a product’s life cycle. The product’s embodied energy is calculated using a global analysis. – Source: Xella-Thermopierre
Latest
Fill out my online form.



