-
 POP3
POP3
-
 Beaufort scale
Beaufort scale
-
 InnoDB
InnoDB
-
 Google Earth
Google Earth
-
 External haemorrhoid
External haemorrhoid
-
 ISP
ISP
-
 Hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
-
 Breast-feeding
Breast-feeding
-
 LPS
LPS
-
 Epidural
Epidural
-
 Quasar
Quasar
-
 Ecosystem
Ecosystem
-
 Systemic antifungal
Systemic antifungal
-
 Passive continental margin
Passive continental margin
-
 LCROSS
LCROSS
-
 Anemophily
Anemophily
-
 Fibrous root system
Fibrous root system
-
 Adware
Adware
-
 Reduction
Reduction
-
 Aldolase
Aldolase
-
 GNU
GNU
-
 Defecation
Defecation
-
 Speleology
Speleology
-
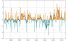 NAO
NAO
-
 Fasciculation
Fasciculation
-
 Gallbladder
Gallbladder
-
 Polymerase
Polymerase
-
 Automaton
Automaton
-
 Clay stone
Clay stone
-
 Hypergolic
Hypergolic
Lake Titicaca
Lake Titicaca lies between the borders of Bolivia and Peru at an altitude of 3636 metres. It is the highest navigable area in the world, with a surface area of 8562 km² for 264 x 65 kilometres, and has around forty islands, some of which are inhabited. Its maximum depth is 280 metres.
The word Titicaca comes from Titi Khar'ka, a rock on the Isla del Sol, and means Rock of the Puma in Aymaran. The Isla del Sol is considered to be the true centre of Inca mythology.
The basin of lake Titicaca is a very old centre of civilisation, and from its Bolivian banks and the vast plateaux rising above them that the Tianhuanaco civilisation spread between the years 600 and 1000 AD, and subsequently greatly inspired the Incas.
The floating islands of the Uros are a unique place in the world, named after the Indians who used to live there. They are still inhabited by many aboriginal people. Built on stilts made from eucalyptus trunks, the rest of the construction is made from reeds, which are the primary local resource, since they are also edible. The houses, schools and the ground itself are all made of reeds. The inhabitants live mainly from fishing, bird hunting, and from harvesting lakeside plants.
Among the other islands, there is Taquile island, of which the inhabitants manage all the tourist activities themselves in such a way as not to interfere with their own way of life. There are no hotels, but you can spend the night at an inhabitant's house, the Taquile people having a reputation for being extremely hospitable.
Amantani island is set to become one of the tourist hotspots of South America. The Andean society that lives there has kept many secular traditions, and is particularly appreciated its decorative gardens and climbing plants. There are also some archaeological remains.
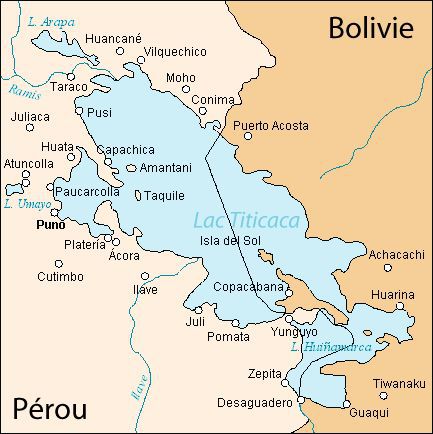 Lake Titicaca.
Lake Titicaca.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



