-
 Pneumatophore
Pneumatophore
-
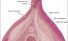 Clitoris
Clitoris
-
 Swallowtail
Swallowtail
-
 M15
M15
-
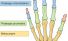 Metacarpus
Metacarpus
-
 Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2
-
 Crystal symmetry
Crystal symmetry
-
 Sodium
Sodium
-
 Diplopia
Diplopia
-
 Caffeine
Caffeine
-
 Transmission line
Transmission line
-
 Roof drain
Roof drain
-
 Ariel
Ariel
-
 Age pyramid
Age pyramid
-
 Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia
-
 Diaclase
Diaclase
-
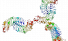 Proteoglycan
Proteoglycan
-
 Hypothenar eminence
Hypothenar eminence
-
 Farad
Farad
-
 Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion
-
 Livery
Livery
-
 Hooke's law
Hooke's law
-
 Dialysis
Dialysis
-
 I.Q.
I.Q.
-
 Accommodation
Accommodation
-
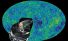 GZK limit
GZK limit
-
 Androgen
Androgen
-
 Key management
Key management
-
 Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
-
 Formal language
Formal language
Fjord
A fjord is a very deep flooded glacial valley with steeply sloping banks. Its mouth is often closed off at a shallow threshold formed by a moraine.
Characteristics of fjord water
Because of their special topography, the waters of fjords are highly stratified:
- at the surface there is a layer of almost fresh water which is rich in oxygen and nutrients. Low in density and calm, this water mixes very little with the underlying salt water;
- deeper down there is normally saline water. The calmness of the water and the barrier provided by the threshold and the surface layer of fresh water severely limit exchanges with the adjoining sea. This water therefore remains in place for a very long time.
The dangers associated with these features
The stagnation of the deep water associated with the absence of light make this water an anoxic and oligotrophic environment. The contamination of this water by pollutants has long-lasting effects, the dilution and biodegrading of these pollutants being extremely slow.
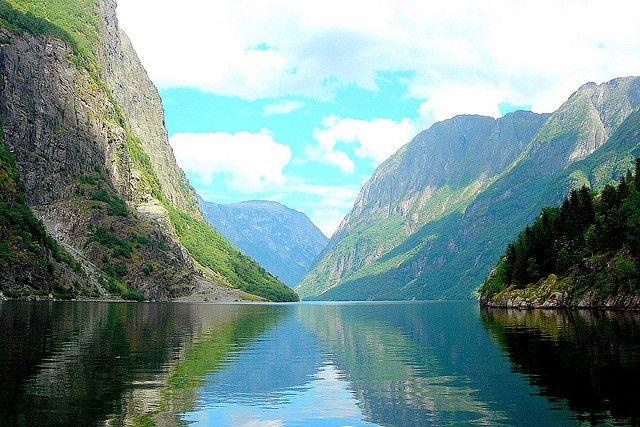 Morphology of a typical Norwegian fjord. © Ken Douglas/Today is a good day CC by-nc-nd 2.0
Morphology of a typical Norwegian fjord. © Ken Douglas/Today is a good day CC by-nc-nd 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



