-
 Cellular automaton
Cellular automaton
-
 Modulation
Modulation
-
 Incretin modulators
Incretin modulators
-
 Transgenesis
Transgenesis
-
 Dermatologist
Dermatologist
-
 Trophallaxis
Trophallaxis
-
 Cyclosilicates
Cyclosilicates
-
 Parallax
Parallax
-
 Sweet Gum tree
Sweet Gum tree
-
 Slurry
Slurry
-
 Indehiscent
Indehiscent
-
 Stamen
Stamen
-
 Arthritis
Arthritis
-
 Eyebrow
Eyebrow
-
 Oceanic zone
Oceanic zone
-
 Container return scheme
Container return scheme
-
 WAP
WAP
-
 Gunning
Gunning
-
 Interleukin
Interleukin
-
 Black ice
Black ice
-
 Mesostase
Mesostase
-
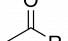 Acetylation
Acetylation
-
 Bamako Convention
Bamako Convention
-
 Oxidase
Oxidase
-
 Alkaline
Alkaline
-
 Fairing
Fairing
-
 Durability
Durability
-
 Nicolaier bacillus
Nicolaier bacillus
-
 Beak
Beak
-
 Vector processor
Vector processor
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is a eukaryotic cellular organelle located in the nucleus.
Structure of the nucleolus
The nucleolus is a region of the nucleus which can be seen under light microscopy (using basic dyes) and electron microscopy (it is dense to electrons). The nucleolus is considered to be an organelle but is not, however, surrounded by a lipid membrane and is not therefore physically separated from the nucleus.
It is usually single but several copies may be present depending on its activity and it may disappear during cell division.
Function of the nucleolus
The nucleolus is where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is transcribed by the enzyme RNA polymerase 1. These rRNA (18S, 5.8S and 28S) are involved in the production of the ribosomes in combination with ribosomal proteins through a process which is also facilitated by factors contained in the nucleolus
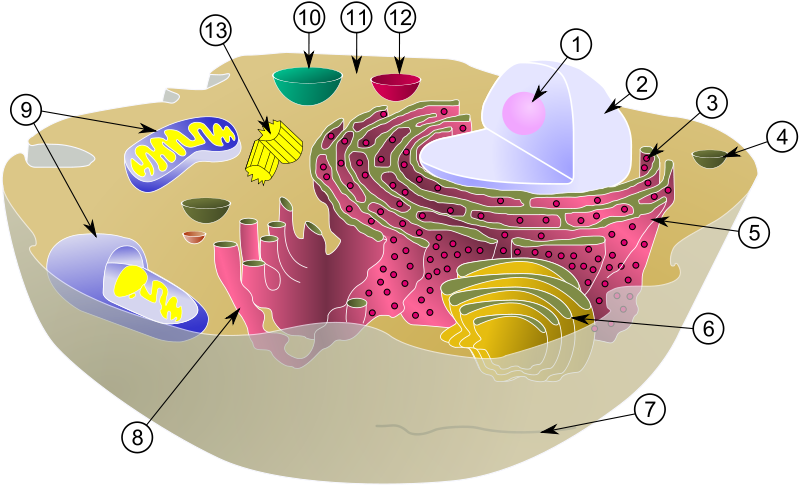 Diagram of a typical animal cell with its organelles: 1. Nucleolus ; 2. Nucleus ; 3. Ribosome ; 4. Vesicle ; 5. Rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum , also called ergastoplasm ; 6. Golgi apparatus; 7. Cytoskeleton ; 8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ; 9. Mitochondrium ; 10. Vacuole ; 11. Cytosol ; 12. Lysosome ; 13. Centriole. © MesserWoland and Szczepan1990, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Diagram of a typical animal cell with its organelles: 1. Nucleolus ; 2. Nucleus ; 3. Ribosome ; 4. Vesicle ; 5. Rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum , also called ergastoplasm ; 6. Golgi apparatus; 7. Cytoskeleton ; 8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ; 9. Mitochondrium ; 10. Vacuole ; 11. Cytosol ; 12. Lysosome ; 13. Centriole. © MesserWoland and Szczepan1990, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



