-
 LCD
LCD
-
 Autosomal
Autosomal
-
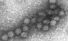 West Nile Virus
West Nile Virus
-
 Blog
Blog
-
 Balneotherapy
Balneotherapy
-
 Aldebaran
Aldebaran
-
 Kyphosis
Kyphosis
-
 Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis
-
 Propolis
Propolis
-
 Nucleolinus
Nucleolinus
-
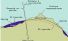 Geoid
Geoid
-
 Oviparous
Oviparous
-
 UMTS
UMTS
-
 Beta-thalassaemia
Beta-thalassaemia
-
 ActiveX
ActiveX
-
 CHAP
CHAP
-
 Equator of a celestial body
Equator of a celestial body
-
 Van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
-
 Charm quark
Charm quark
-
 Crystallography
Crystallography
-
 Yersin bacillus
Yersin bacillus
-
 Gap
Gap
-
 Noma
Noma
-
 Deletion
Deletion
-
 Lock
Lock
-
 Boxwork
Boxwork
-
 Digestion
Digestion
-
 Engine torque
Engine torque
-
 Second order parametric interactions
Second order parametric interactions
-
 Anhydrobiosis
Anhydrobiosis
SATA
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment: connection bus between the motherboard and a mass storage device such as a hard drive.
The adoption of the serial mode was an evolution of the ATA bus, still known as IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) and from now on as opposed to P-ATA, Parallel ATA.
The SATA standard was introduced in 2003, and made an increase in transfer speed possible. The theoretical transfer rate is 150MB/s and 300 MB/s for SATA version II, compared with 133MB/s for P-ATA with the Ultra DMA protocol.
Ironically, the previous parallel connection allowed higher transfer rates. But the logic was reversed by the increased speed at which the electronics run. On a series link, a series of bits can be sent at very high frequencies that a parallel link would not be able to handle.
The series mode has other advantages too: smaller cables and connectors and a longer maximum cable length.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



