-
 Rowan
Rowan
-
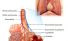 Pulmonary alveolus
Pulmonary alveolus
-
 Black ice
Black ice
-
 Kennedy Space Center
Kennedy Space Center
-
 Black hole
Black hole
-
 Shingle
Shingle
-
 Levorotatory
Levorotatory
-
 Celery
Celery
-
 Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis
-
 Topocentric
Topocentric
-
 Single-stranded
Single-stranded
-
 Smoltification
Smoltification
-
 Group velocity
Group velocity
-
 Opiate antitussive
Opiate antitussive
-
 One-way paging
One-way paging
-
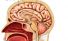 Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
-
 Graph theory
Graph theory
-
 Dorsiflexion
Dorsiflexion
-
 Hallux
Hallux
-
 In vitro
In vitro
-
 Carbon credit
Carbon credit
-
 Diploblastic
Diploblastic
-
 Ekpyrotic cosmology
Ekpyrotic cosmology
-
 VBR
VBR
-
 Scrapie
Scrapie
-
 bps bits per second
bps bits per second
-
 Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
-
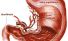 Pylorus
Pylorus
-
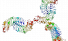 Proteoglycan
Proteoglycan
-
 Thalassaemia
Thalassaemia
ATM
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is network technology that appeared at the beginning of the 1990s to handle voice, video and data transport with a guaranteed quality of service.
ATM uses a switching technique that is midway between circuit switching (telephony) and packet switching (X25). The cells are switched within the hardware, defining virtual circuits.
The information is sent in fixed length packets called "cells". 53 bits of which 5 header bits.
Current switches support 16 ports at 155Mbit/s or 24 ports at 100Mbit/s, giving a total of 2.4Gbit/s.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



