-
 Edaphic
Edaphic
-
 Narcotic
Narcotic
-
 Lock
Lock
-
 Viral culture
Viral culture
-
 Autonomous
Autonomous
-
 Hawking radiation
Hawking radiation
-
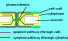 Symplast
Symplast
-
 Bearded seal
Bearded seal
-
 NASA
NASA
-
 Mascarene petrel
Mascarene petrel
-
 Blogroll
Blogroll
-
 Chain reaction
Chain reaction
-
 ADEME
ADEME
-
 Fumarole deposits
Fumarole deposits
-
 Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia
-
 Thrust
Thrust
-
 Spectral classification
Spectral classification
-
 GSTP
GSTP
-
 Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome
-
 Missing link
Missing link
-
 Embossing
Embossing
-
 Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
-
 Hadron
Hadron
-
 Black body
Black body
-
 Xbox Live
Xbox Live
-
 Shark feeding
Shark feeding
-
 Stream bed
Stream bed
-
 Tide
Tide
-
 Penicillin
Penicillin
-
 Vitamin A
Vitamin A
Osmolarity
Osmolarity is defined as the number of particles per litre of solution, or more accurately, the number of moles in solution that contribute to the osmotic pressure exerted on a membrane during osmosis. It is therefore a quantity involved in the definition of osmotic pressure.
It is measured in osmoles per litre. An osmole is a mole of particles in solution. For example, a solution of 1 mol/L of NaCl corresponds to an osmolarity of 2 osmol/L. It must be remembered that not all osmoles are necessarily osmotically active particles.
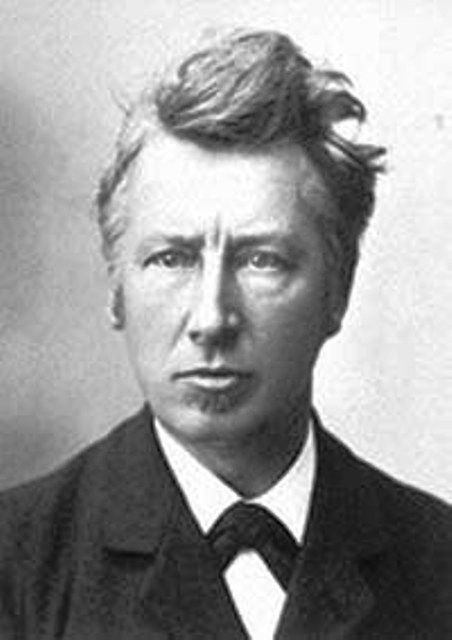 Jacobus Henricus Van't Hoff was a Dutch chemist. He was awarded the Nobel prize for chemistry and explained osmotic pressure. © Wikipedia_public domain
Jacobus Henricus Van't Hoff was a Dutch chemist. He was awarded the Nobel prize for chemistry and explained osmotic pressure. © Wikipedia_public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



