-
 Urushiol
Urushiol
-
 Reverse genetics
Reverse genetics
-
 M15
M15
-
 Passphrase
Passphrase
-
 Cementation
Cementation
-
 Phase diagram
Phase diagram
-
 Sea ice - Grey
Sea ice - Grey
-
 Desert pavement or reg
Desert pavement or reg
-
 Organic phosphate group
Organic phosphate group
-
 Grid computing
Grid computing
-
 Monospecific
Monospecific
-
 Blu-Ray
Blu-Ray
-
 Procambium
Procambium
-
 Siderophilic
Siderophilic
-
 X-15
X-15
-
 Artificial meadow
Artificial meadow
-
 Galactan
Galactan
-
 Agroenergy
Agroenergy
-
 DVB-SH
DVB-SH
-
 Solar wind
Solar wind
-
 Cathartic
Cathartic
-
 Small intestine
Small intestine
-
 Canada-France-Hawaii observatory
Canada-France-Hawaii observatory
-
 Photoperiod
Photoperiod
-
 Incandescent light bulb
Incandescent light bulb
-
 Constellation of Pegasus
Constellation of Pegasus
-
 Sperm whale
Sperm whale
-
 SAFER
SAFER
-
 Plug and Play
Plug and Play
-
 Highlighting
Highlighting
Monoethanolamine
Monoethanolamine (MEA), or 2-aminoethanol, is a phospholipid composed of a primary amine and a primary alcohol. This toxic compound is a weak base. It is a viscous liquid that smells of ammonia.
Uses of monoethanolamine
MEA is used in the production of many chemical products such as detergents, emulsifiers and pharmaceutical products.
MEA is also used to reduce the acidity of certain gases and to capture carbon dioxide from post-combustion gases.
MEA to obtain pure carbon dioxide
At ambient temperature a solution of MEA captures gaseous CO2 in the form of salts. The solution is simply heated in a confined enclosure to release the carbon dioxide and regenerate the monoethanolamine solution. Pure carbon dioxide is thus obtained.
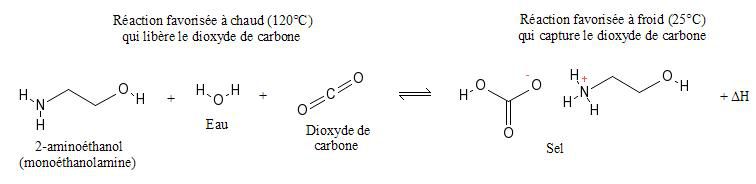
CO2 capture in the presence of monoethanolamine. © A. Halme, Wikimedia CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



