-
 Beta blocker
Beta blocker
-
 Bolometer
Bolometer
-
 P80
P80
-
 Informed consent
Informed consent
-
 Analogy
Analogy
-
 Hour angle
Hour angle
-
 Thermosphere
Thermosphere
-
 Resection
Resection
-
 Webcam
Webcam
-
 Cycline
Cycline
-
 Strawberry
Strawberry
-
 Schweizerhalle disaster
Schweizerhalle disaster
-
 Capsule
Capsule
-
 Epitope
Epitope
-
 Bit
Bit
-
 Platinoids
Platinoids
-
 Uterine relaxant
Uterine relaxant
-
 Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus
-
 Hydroelectric pumping station
Hydroelectric pumping station
-
 Encoder
Encoder
-
 Mesosphere
Mesosphere
-
 Teraflops
Teraflops
-
 Cryptic
Cryptic
-
 Toxicity
Toxicity
-
 Bose-Einstein Condensate
Bose-Einstein Condensate
-
 Terrestrial planet
Terrestrial planet
-
 Brazing
Brazing
-
 Hawking radiation
Hawking radiation
-
 Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3
-
 Latent
Latent
Hardness of water
The hardness of water gives the concentration of carbonates (CO32-) and strong bases, in other words its alkalinity.
Different scales are used in different countries; in the UK, English degrees (°e) are used and in the USA, ppm, also called American degrees. 1°e is equivalent to 2.39 mg/L of hydroxide ion (HO-) or 4.21 mg/L of carbonate ion, or 8.56 mg/L of bicarbonate ion (HCO3-).
To take into account the bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), the total alkali strength is used. Total hardness is expressed as the sum of the calcium and magnesium concentrations.
Thealkalinity of water is closely related to its hardness and therefore to its corrosive character and capacity to produce scale in pipes.
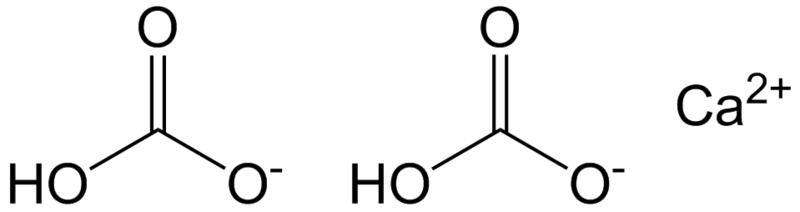
A calcium bicarbonate molecule in solution. Total alkali strength indicates bicarbonate ions. © Epop, Wikimedia public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



