-
 Videoconference
Videoconference
-
 Fuselage
Fuselage
-
 Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian
-
 Lumen
Lumen
-
 Rogue waves
Rogue waves
-
 Oviparous
Oviparous
-
 Lore
Lore
-
 Amine acid group
Amine acid group
-
 Petrified
Petrified
-
 Lithium-bearing
Lithium-bearing
-
 Soft acid
Soft acid
-
 Collenchyma
Collenchyma
-
 Oat
Oat
-
 Adiabatic
Adiabatic
-
 FPS
FPS
-
 Ramjet engine
Ramjet engine
-
 Macrophyte
Macrophyte
-
 Reflecting power
Reflecting power
-
 Pulmonary plague
Pulmonary plague
-
 Haemoccult
Haemoccult
-
 Psycho-oncologist
Psycho-oncologist
-
 M20
M20
-
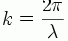 Wavenumber
Wavenumber
-
 Nonlinear crystal
Nonlinear crystal
-
 Tissue
Tissue
-
 M16
M16
-
 Audiotex
Audiotex
-
 Asparagus
Asparagus
-
 Autosome
Autosome
-
 Spectrum
Spectrum
Ethylene
Ethylene (or ethene) is a hydrocarbon with two carbon atoms having the formula C2H4, and molecular formula CH2=CH2 (with a double bond between the two carbon atoms, C).
With its two carbon atoms it is related to ethane (CH3-CH3) and ethanol (CH3-CH2OH, the alcohol in drinks). With its C=C double bond it is the simplest alkene since it only has one bond. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon because it can shed half of this double bond to bind to other atoms or molecules.
Ethylene is a highly reactive gas. It is traditionally obtained by petroleum cracking. Used in many fields, it is the most produced organic molecule in the world. For example, polymerisation yields polyethylene, a very common plastic.
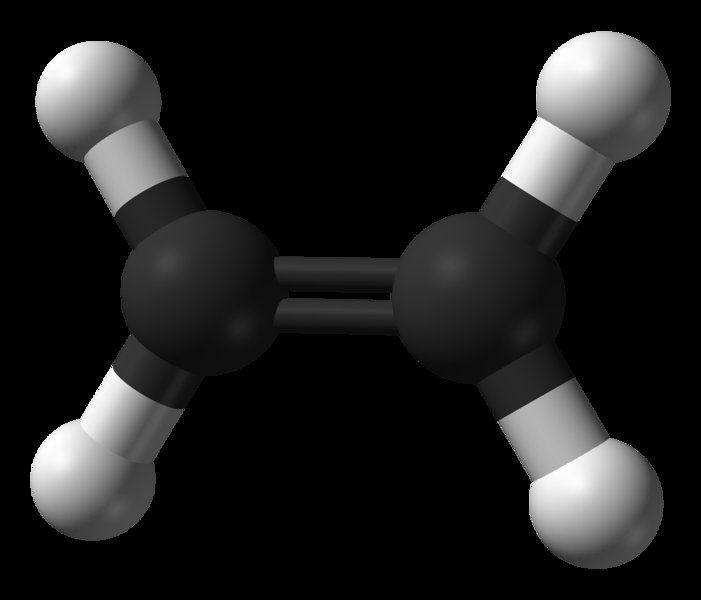 An ethylene molecule. The two carbon atoms (black) held together by the double bond can be seen, as well as the four hydrogen atoms (white). The double bond can become a single bond and each carbon atom can then bond to another atom or molecule. This is how ethylene can be polymerised by binding the molecules to each other. © Public domain
An ethylene molecule. The two carbon atoms (black) held together by the double bond can be seen, as well as the four hydrogen atoms (white). The double bond can become a single bond and each carbon atom can then bond to another atom or molecule. This is how ethylene can be polymerised by binding the molecules to each other. © Public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



